solution Use Case
Grass Valley AMPP – Production Scheduling & Orchestration
GrassValley
At NAB 2025, we showcased our latest integration with Grass Valley AMPP: managing the lifecycle of GV AMPP productions and orchestrating not only all your GV AMPP workloads, but also third-party and offline resources such as people or rooms. Here are the five things we do:
- Open the DataMiner Scheduling app to prepare your production: pick the resources you need, either one by one or by selecting a template.
- DataMiner allocates resources for the upcoming production from resource pools; either fully automated or manually selected by an operator.
- Before the production starts, DataMiner deploys the GV AMPP workloads, configures them, and connects the signals between them. The same applies to any other third-party resources, including ingress and egress signals.
- While the production is running, DataMiner monitors the production and all resources, offering tailored user interfaces for real-time control.
- At the end of the production, DataMiner undeploys all resources and releases them back into the pool. Additionally, it calculates the production costs using rate cards attached to each resource.
With that in place, you only pay for the GV AMPP resources during the production—DataMiner ensures they’re spun up and down at the right time.
Wondering how we do this? The foundation is our latest GV AMPP connector, combined with our dataminer.MediaOps solution, which includes pre-configured user interfaces, workflows, and a standard data model to manage all production data.
USE CASE DETAILS
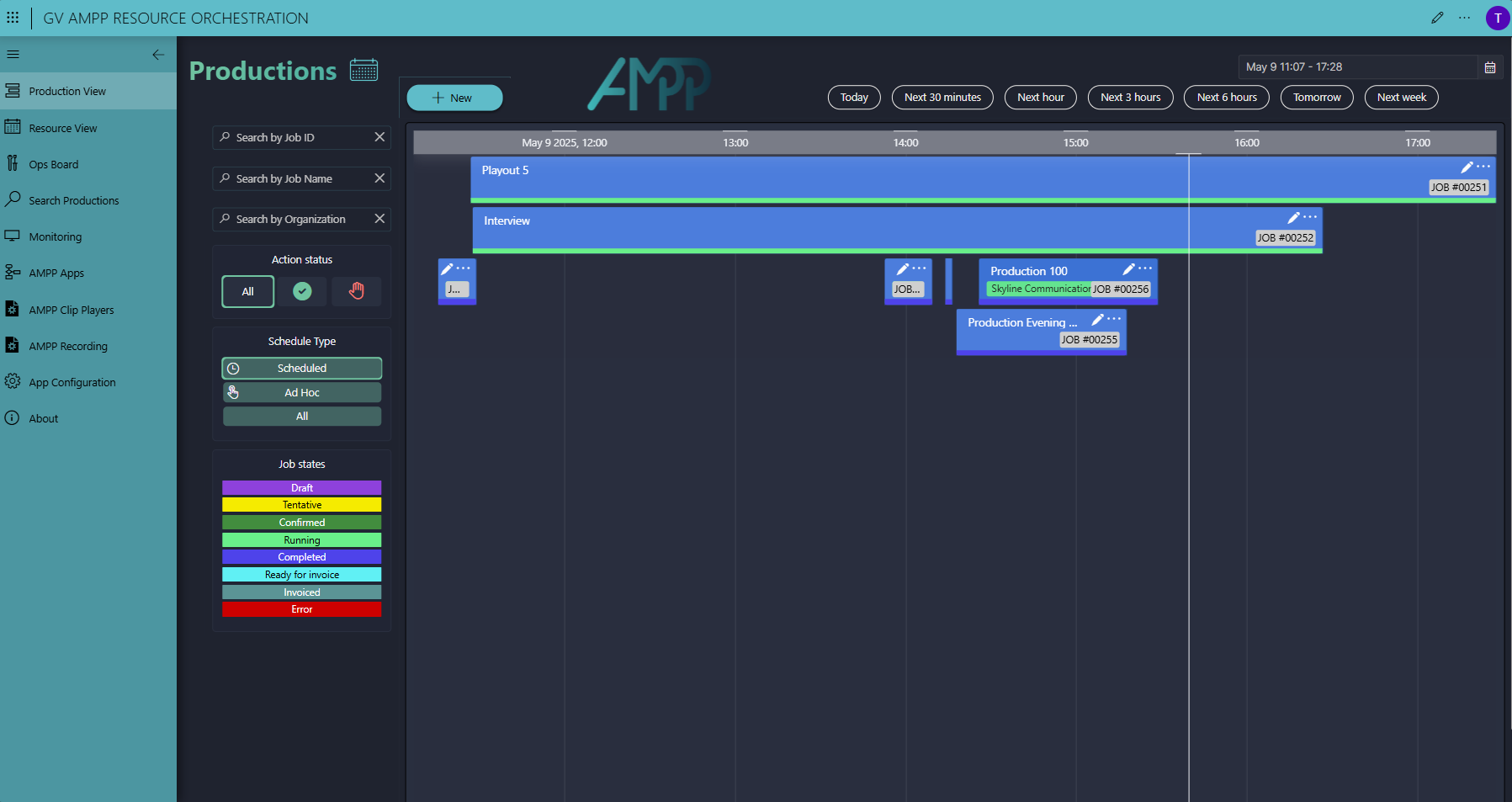
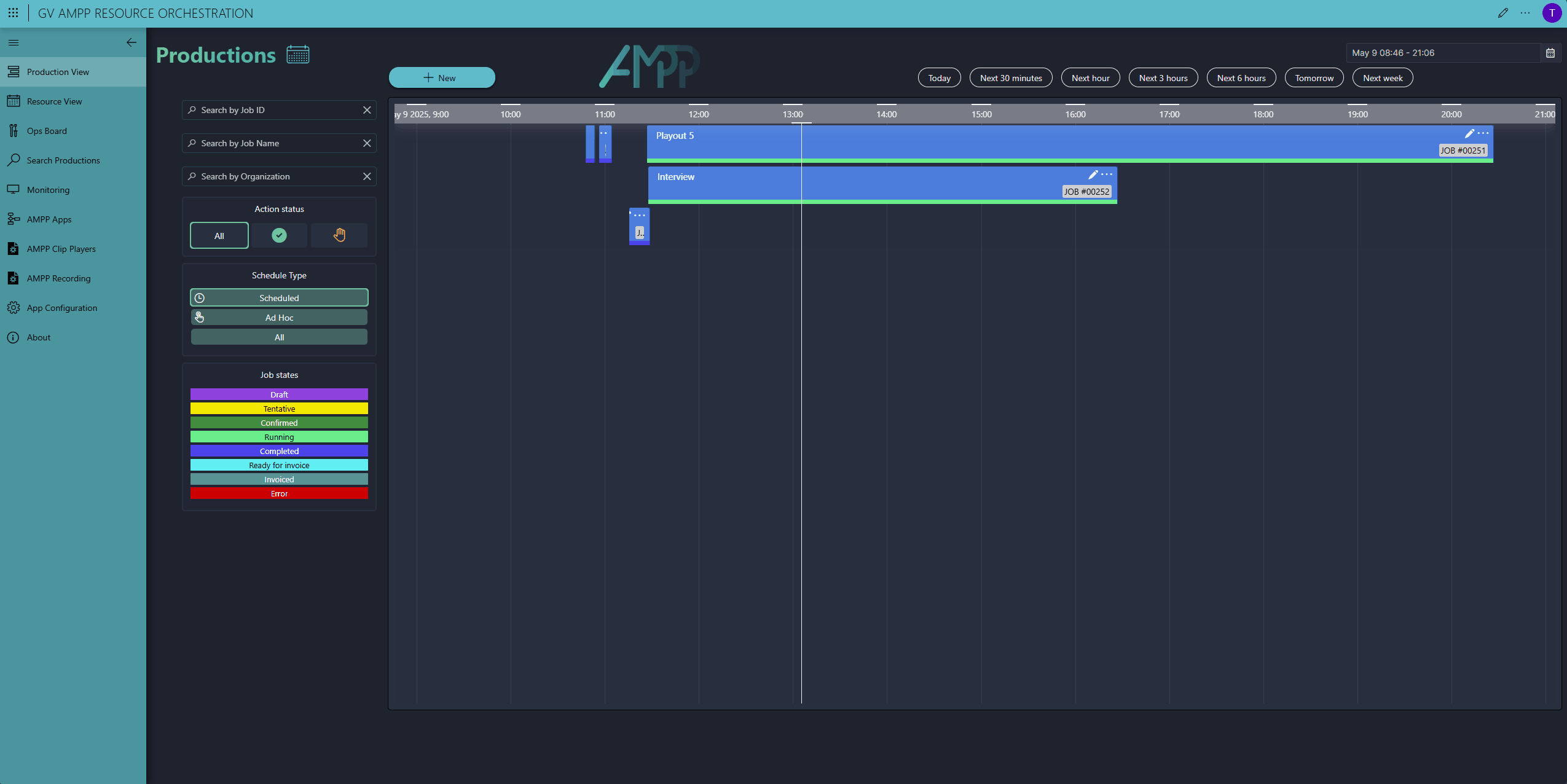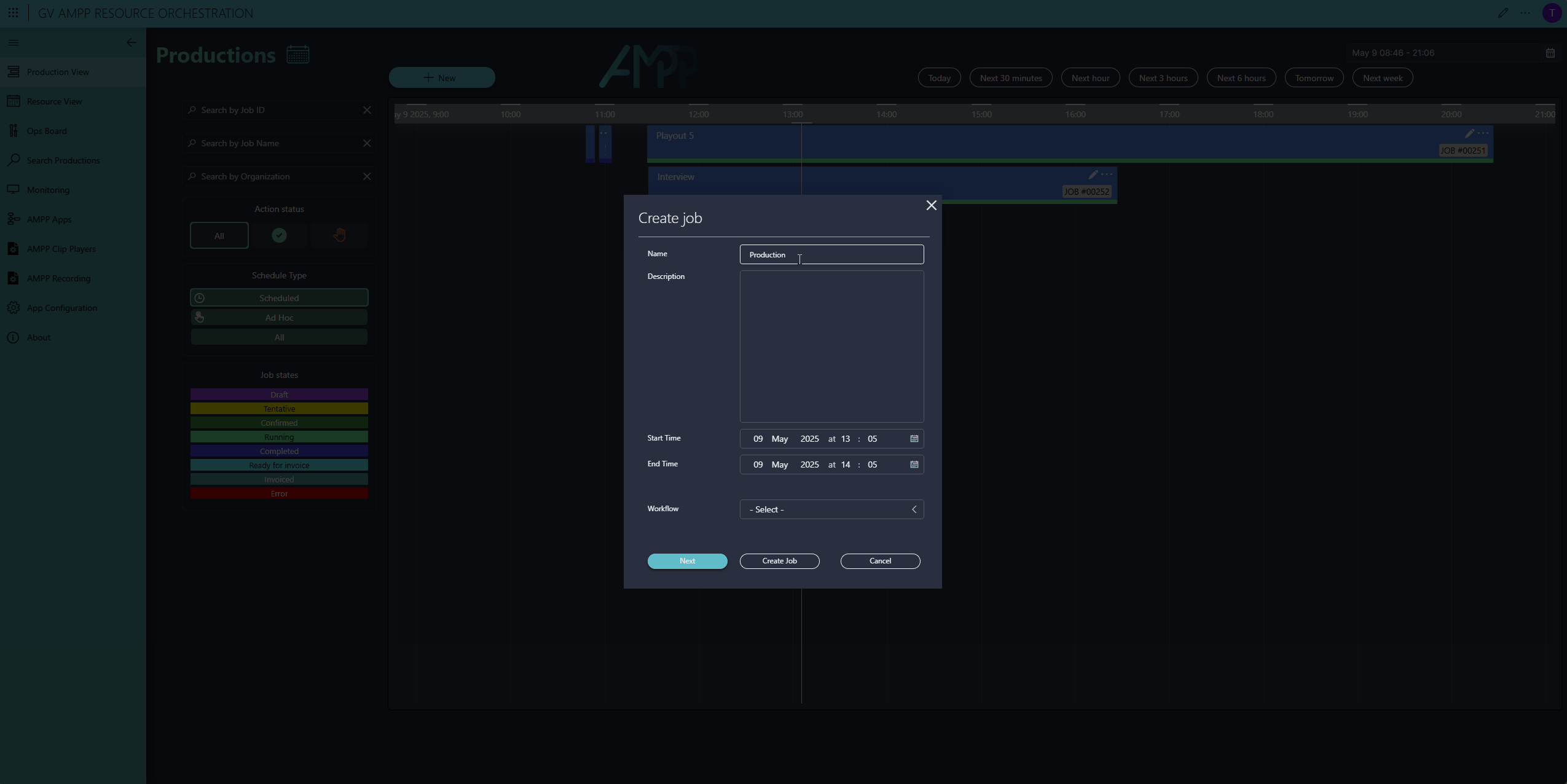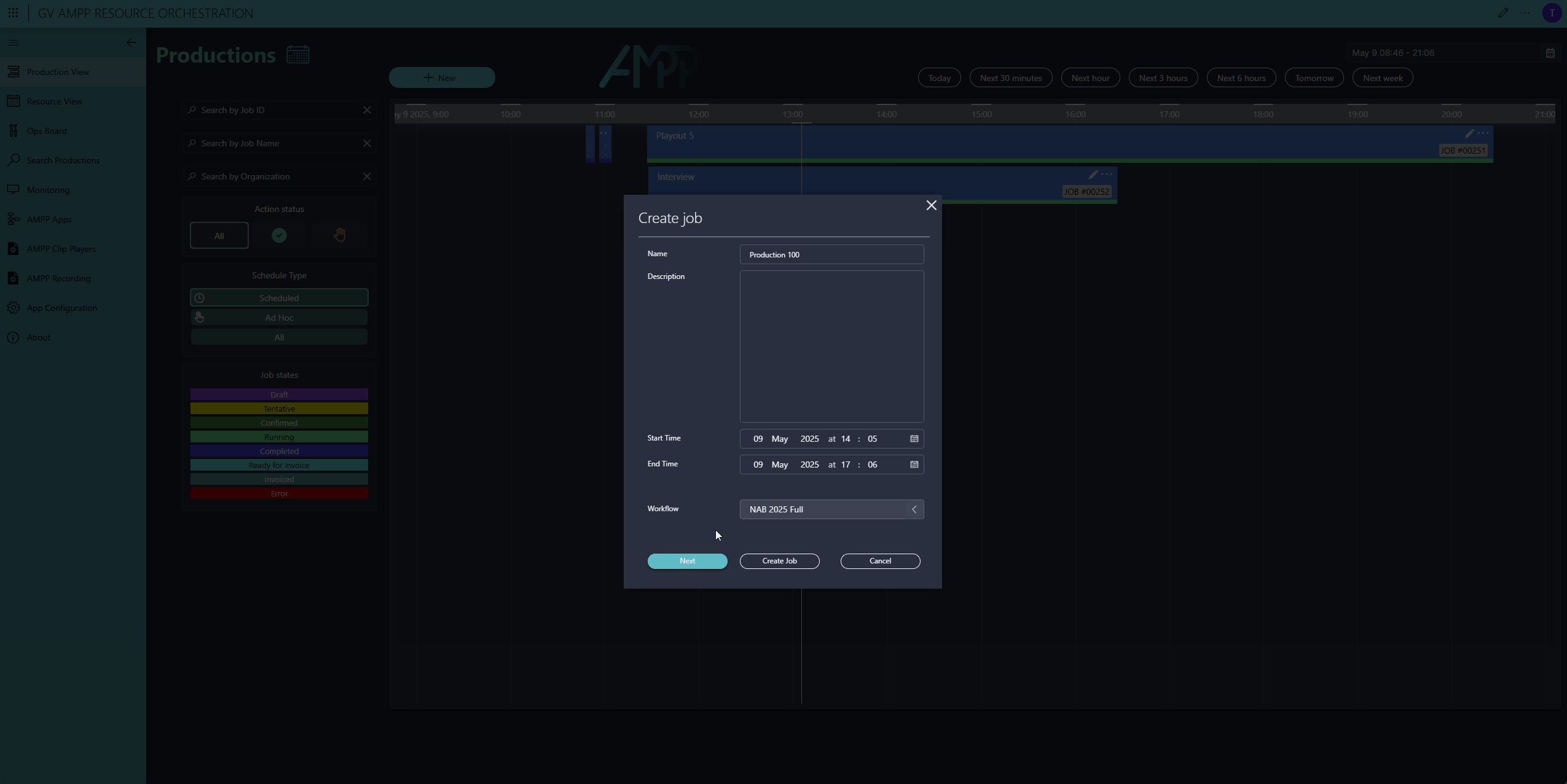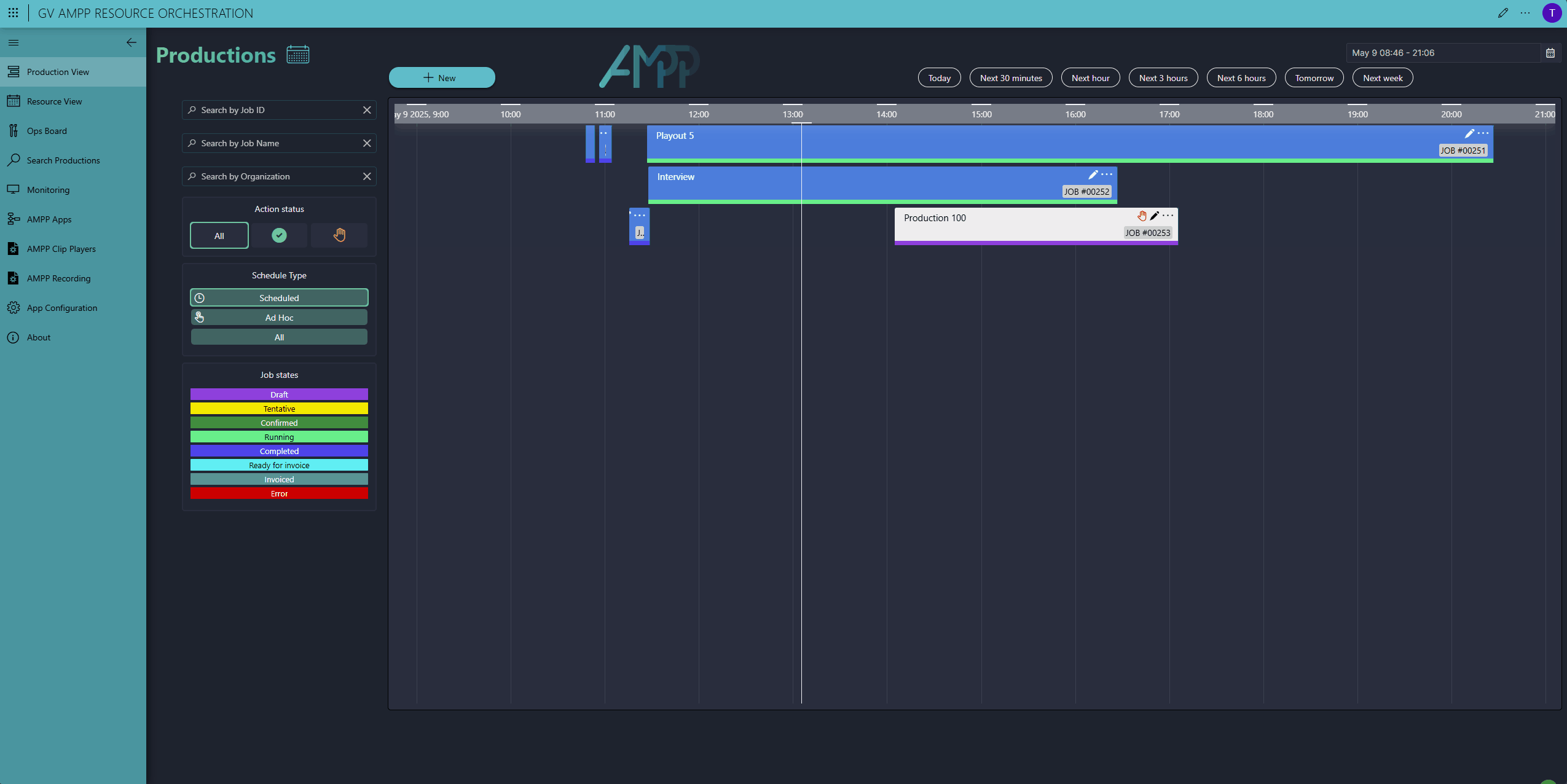 Here you can see our Scheduler app. To add a new production, click the New button in the top-left corner, enter a start and end time, give it a name, and select a production template (we call this a workflow)—that's all here is to it.
Here you can see our Scheduler app. To add a new production, click the New button in the top-left corner, enter a start and end time, give it a name, and select a production template (we call this a workflow)—that's all here is to it.
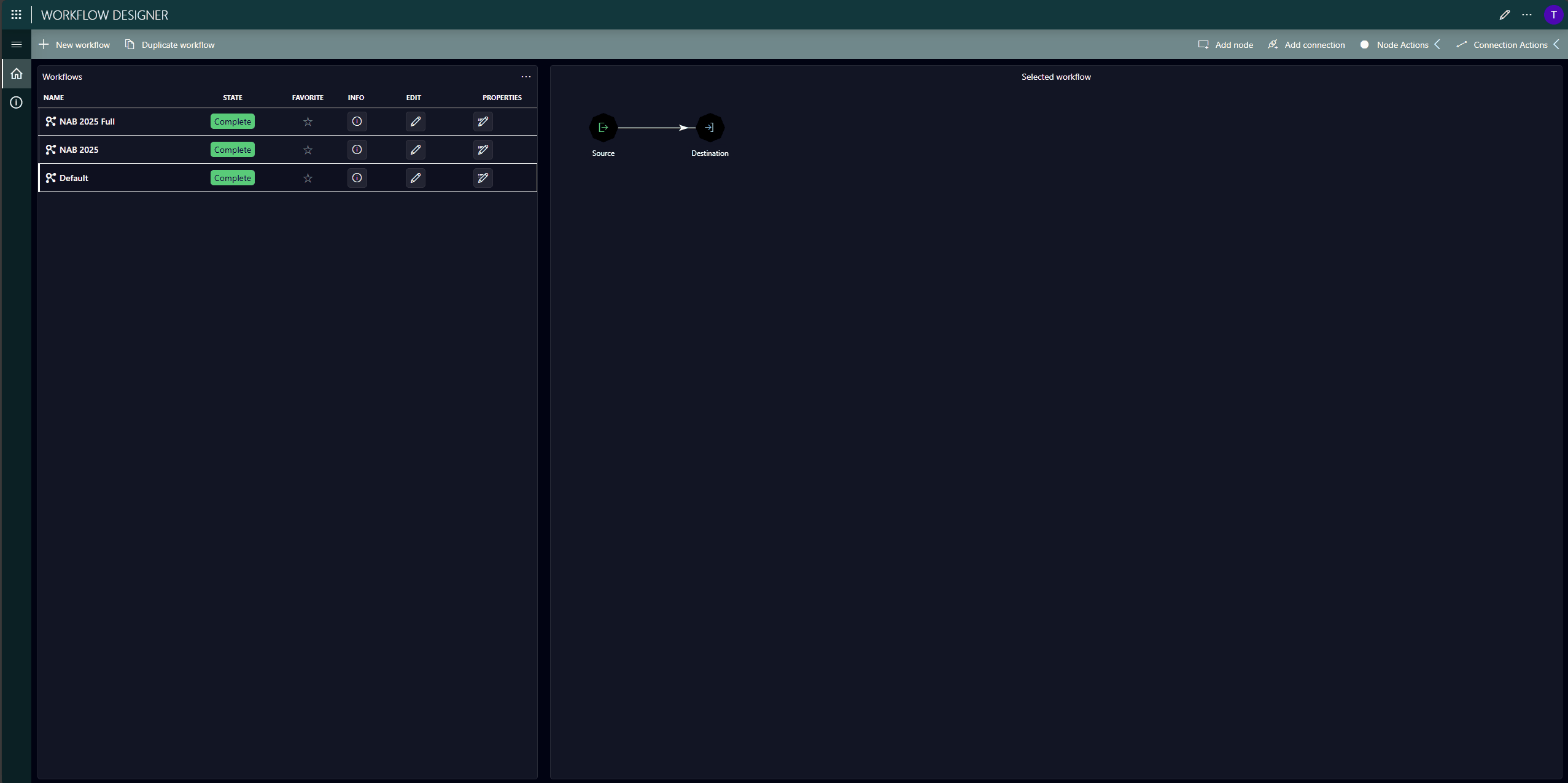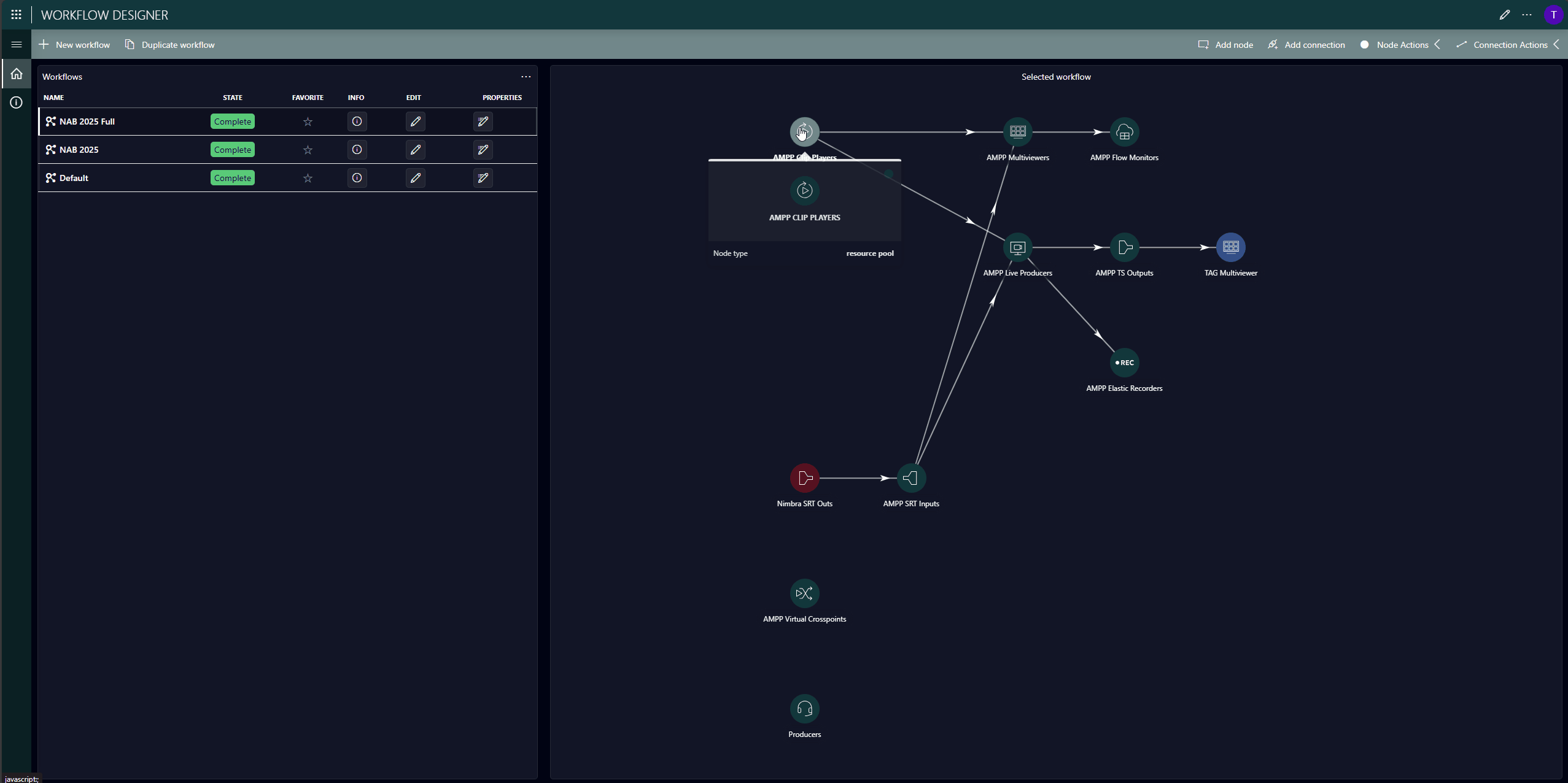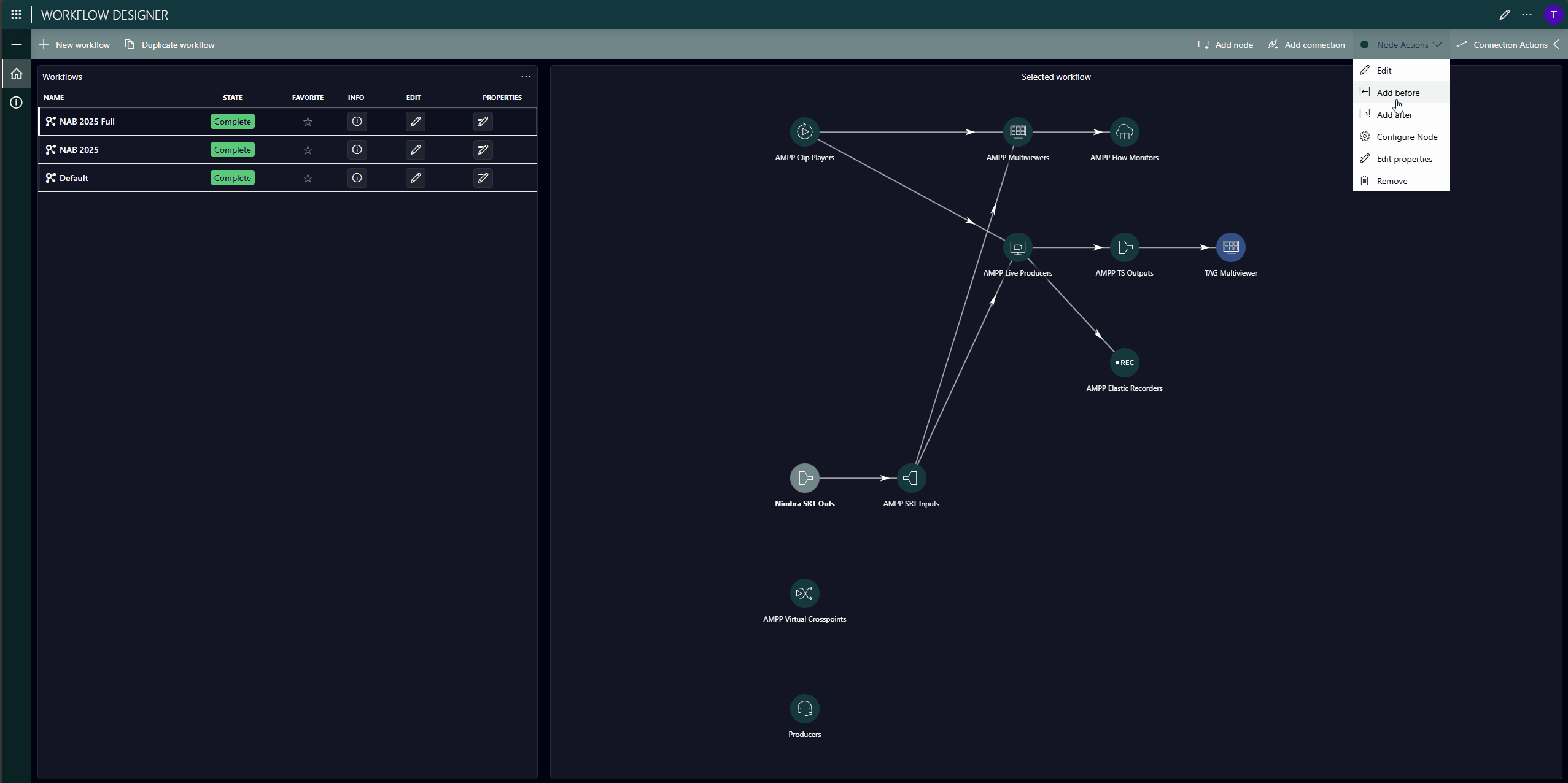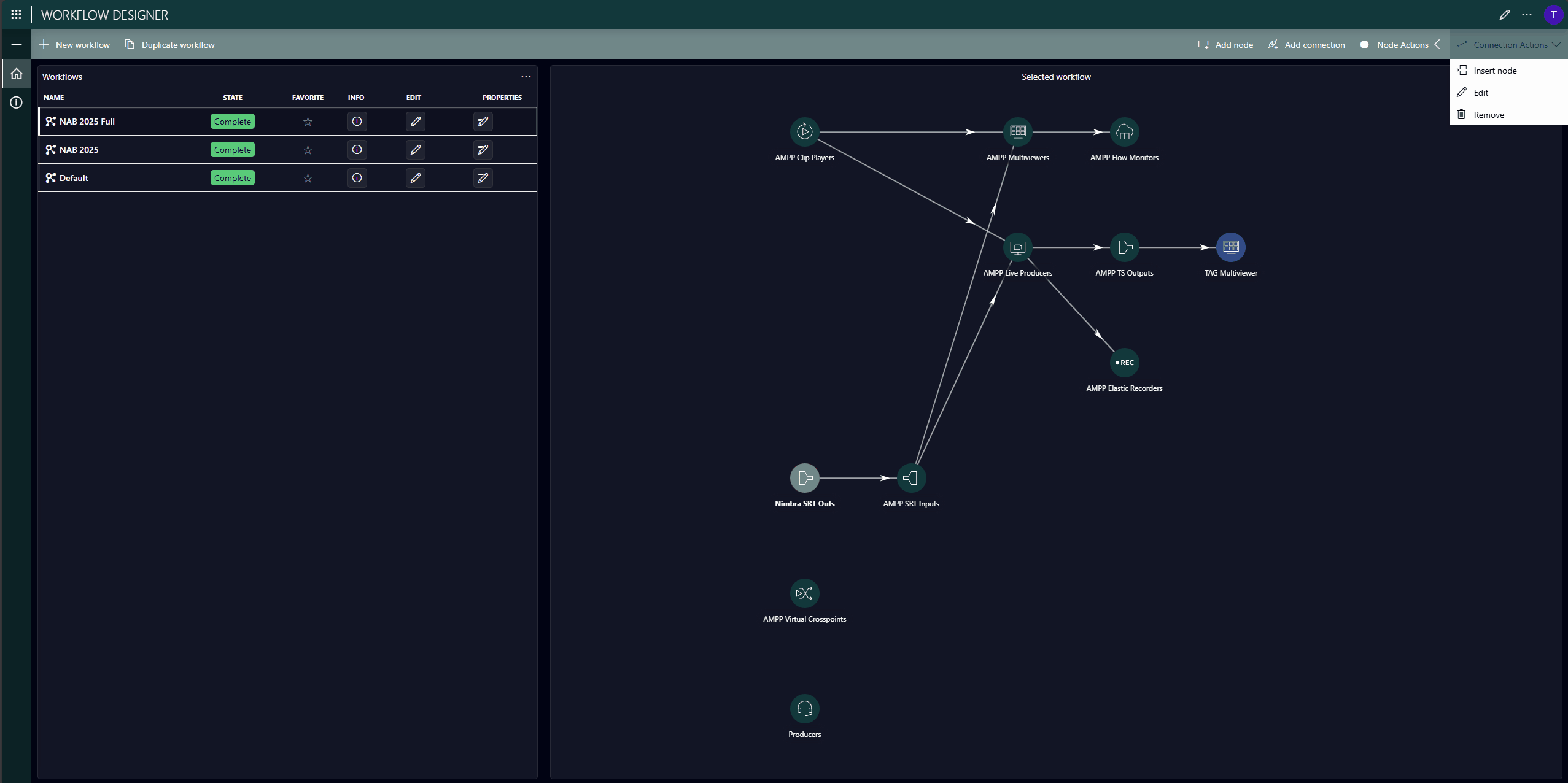 These templates are prepared in the Workflow Designer app and define the type of resource (a resource pool, not a specific resource), the required configuration, and connectivity. In our example, the production includes GV AMPP resources (workloads), as well as other resources such as NimbraEdge SRT streams from NetInsight, a Multiviewer from TAG VS, and even people.
These templates are prepared in the Workflow Designer app and define the type of resource (a resource pool, not a specific resource), the required configuration, and connectivity. In our example, the production includes GV AMPP resources (workloads), as well as other resources such as NimbraEdge SRT streams from NetInsight, a Multiviewer from TAG VS, and even people.
 The red hand icon on the new production indicates that some manual action is still required. For this demo, we chose for the majority of resources to be auto-selected by DataMiner, except for the SRT input and the GV AMPP clip player. These still need to be selected manually by the operator. Note that the operator can only select available resources that meet the requirements to perform the job. Resources already booked for other productions are automatically excluded.
The red hand icon on the new production indicates that some manual action is still required. For this demo, we chose for the majority of resources to be auto-selected by DataMiner, except for the SRT input and the GV AMPP clip player. These still need to be selected manually by the operator. Note that the operator can only select available resources that meet the requirements to perform the job. Resources already booked for other productions are automatically excluded.
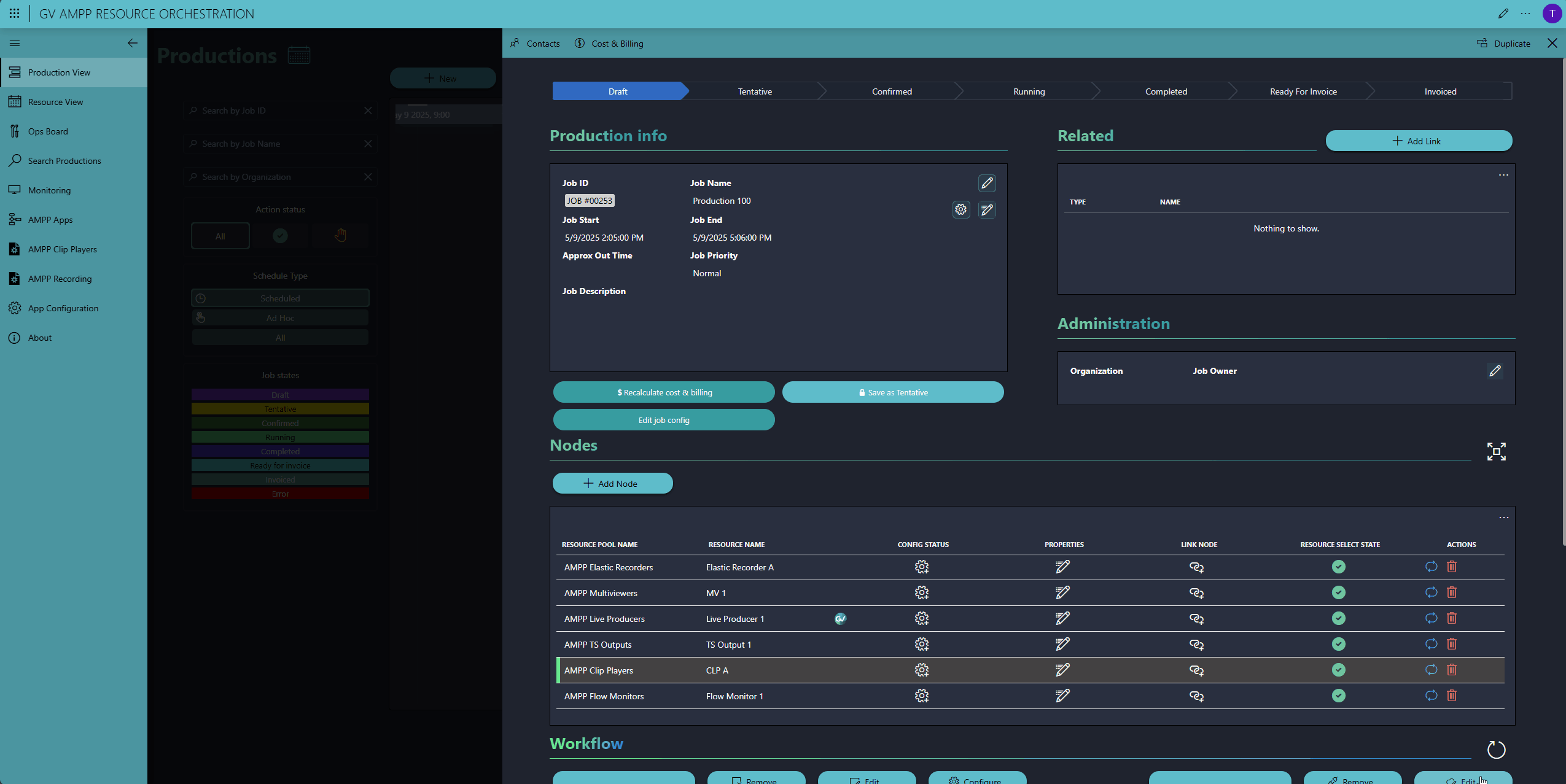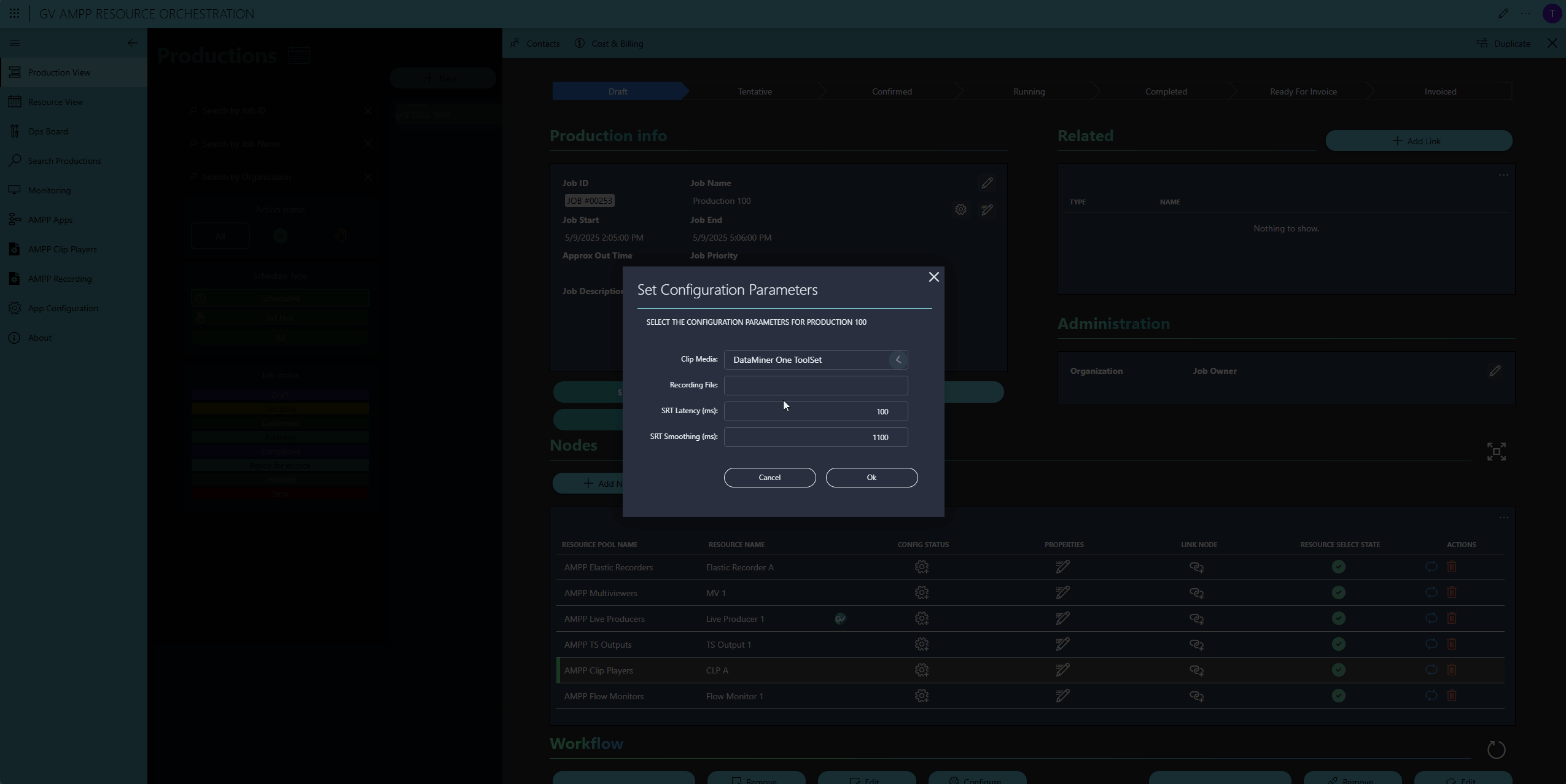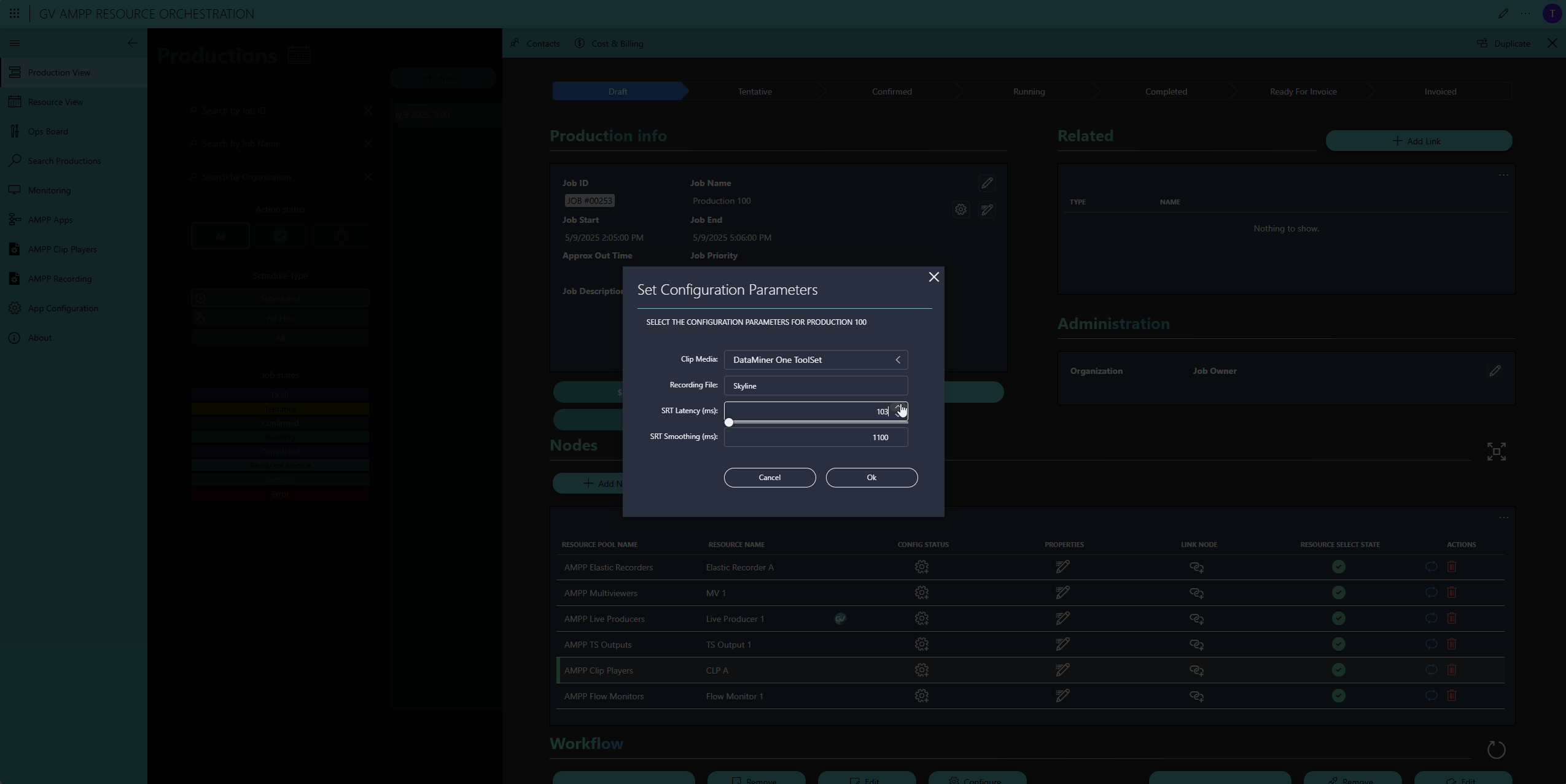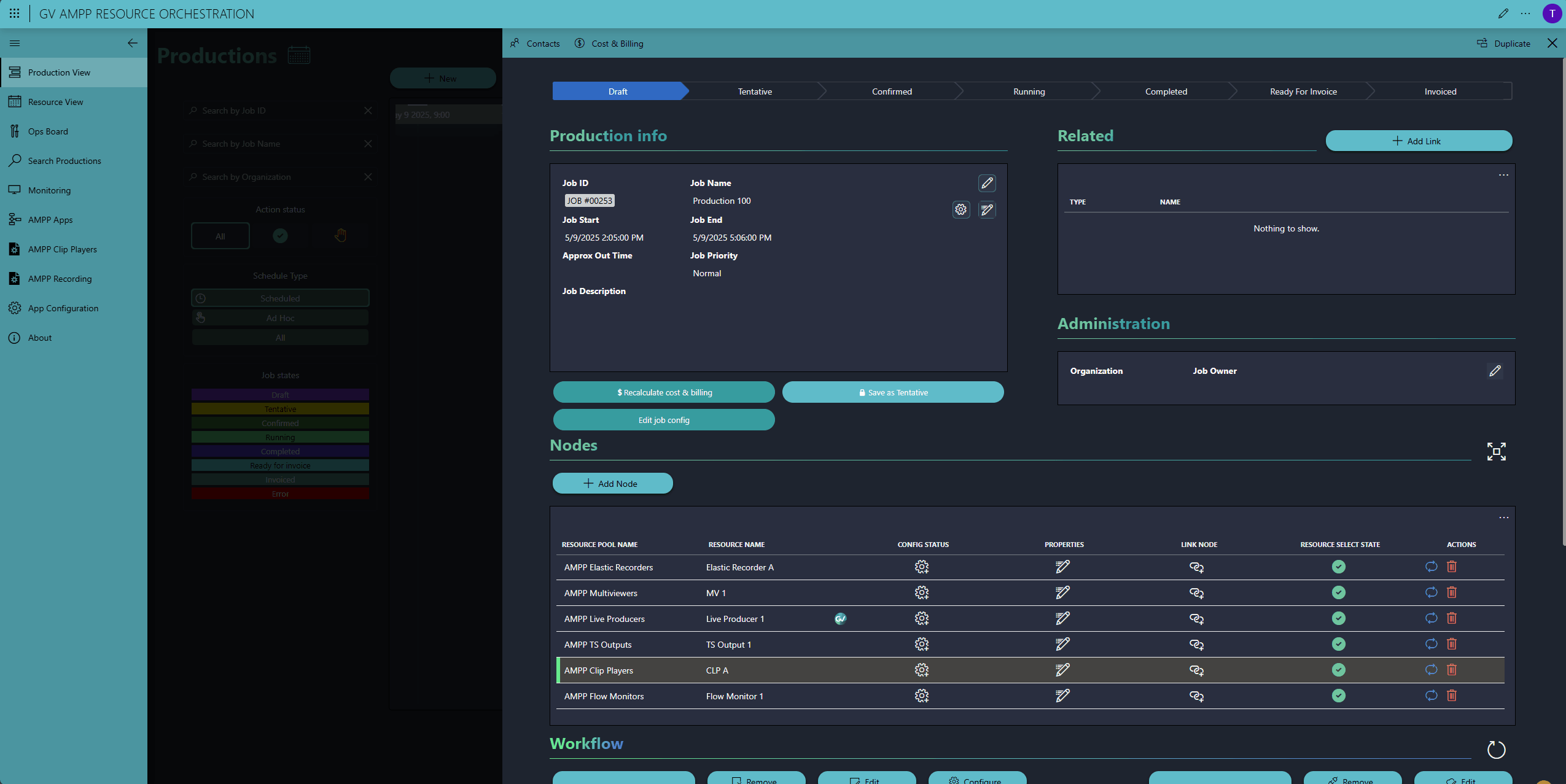 In the next step, operators can add configuration parameters—for example, selecting a video clip for the player, naming the recorded clip on the Elastic Recorder, or configuring the SRT latency.
In the next step, operators can add configuration parameters—for example, selecting a video clip for the player, naming the recorded clip on the Elastic Recorder, or configuring the SRT latency.
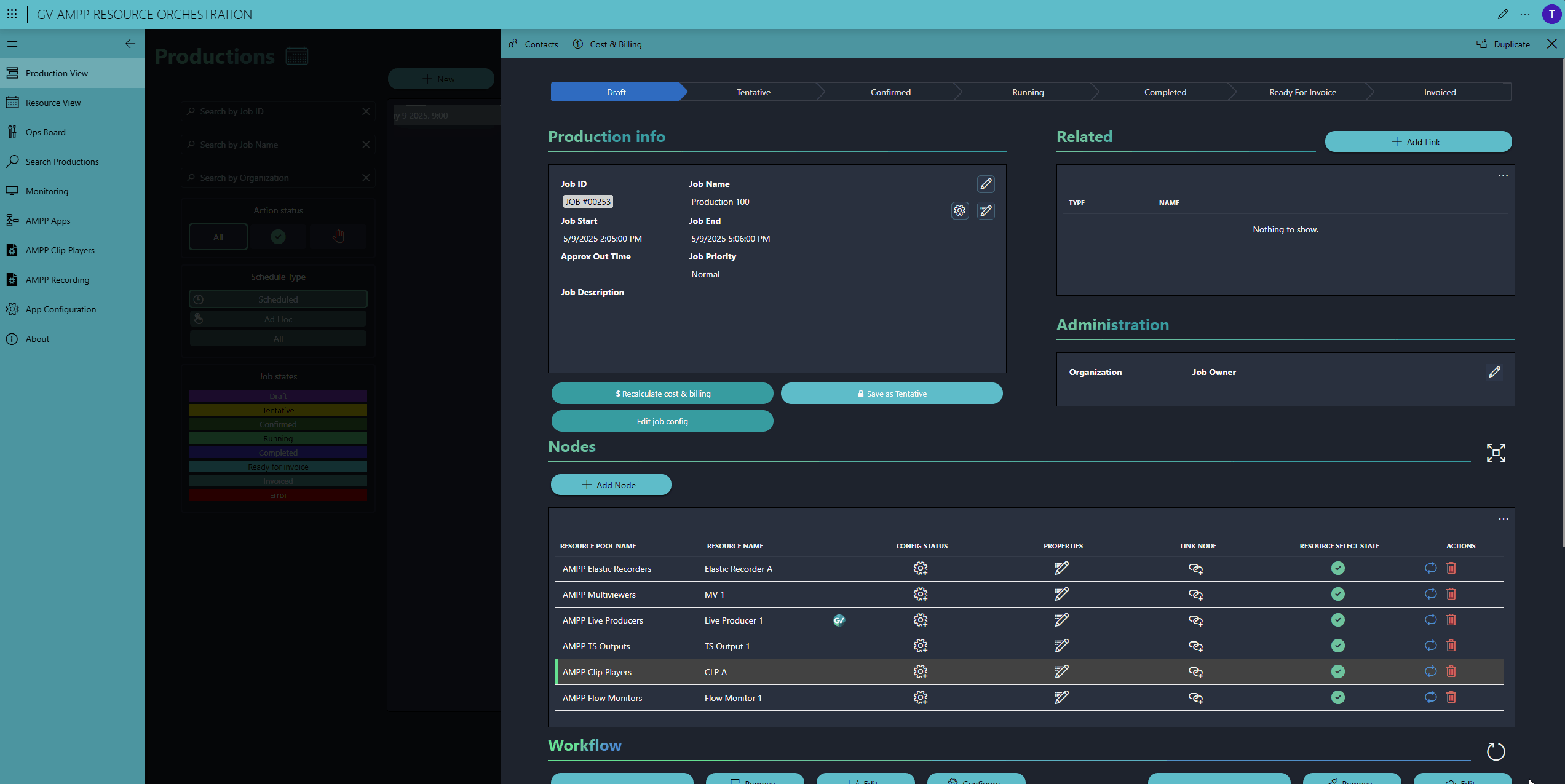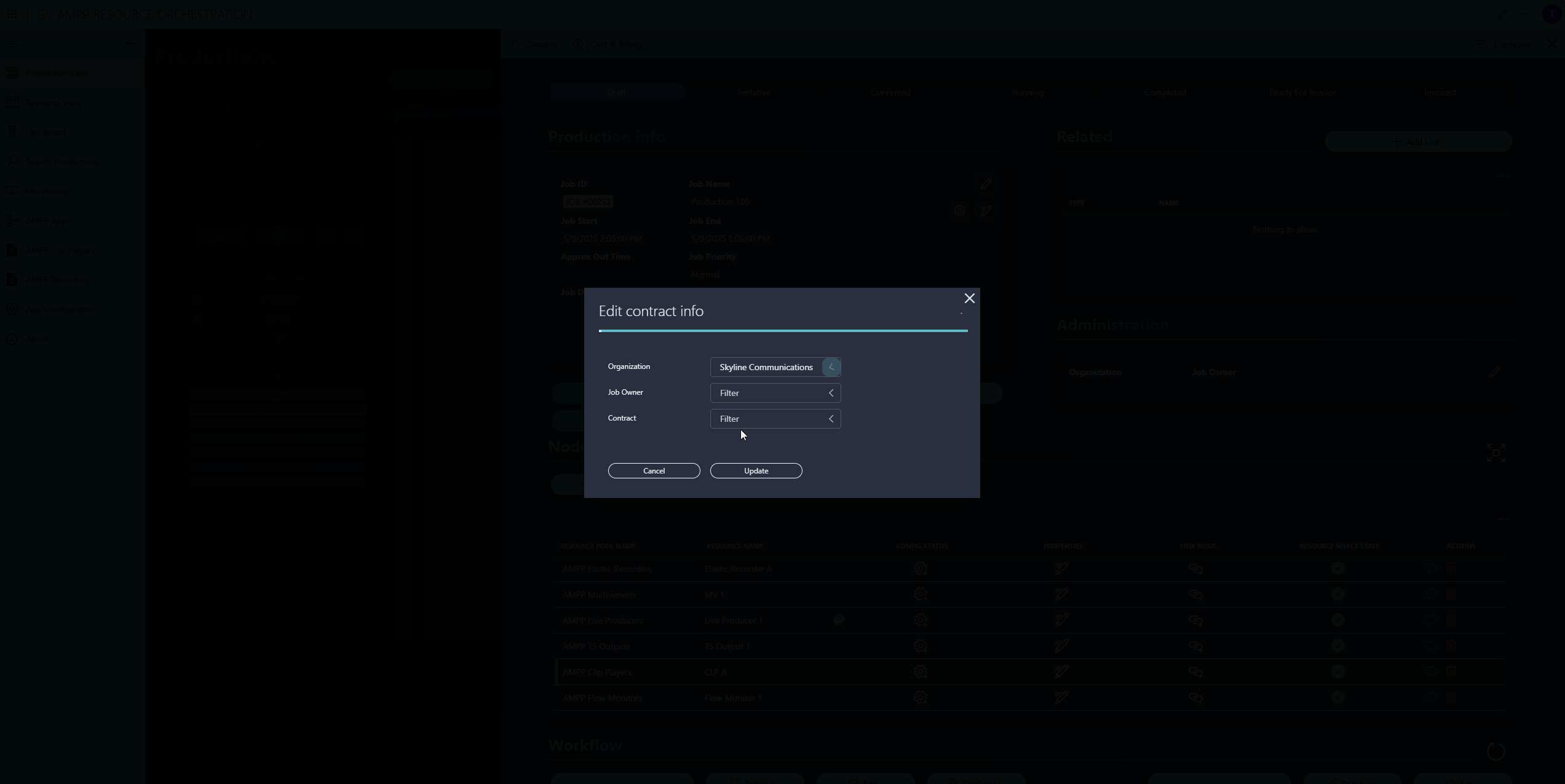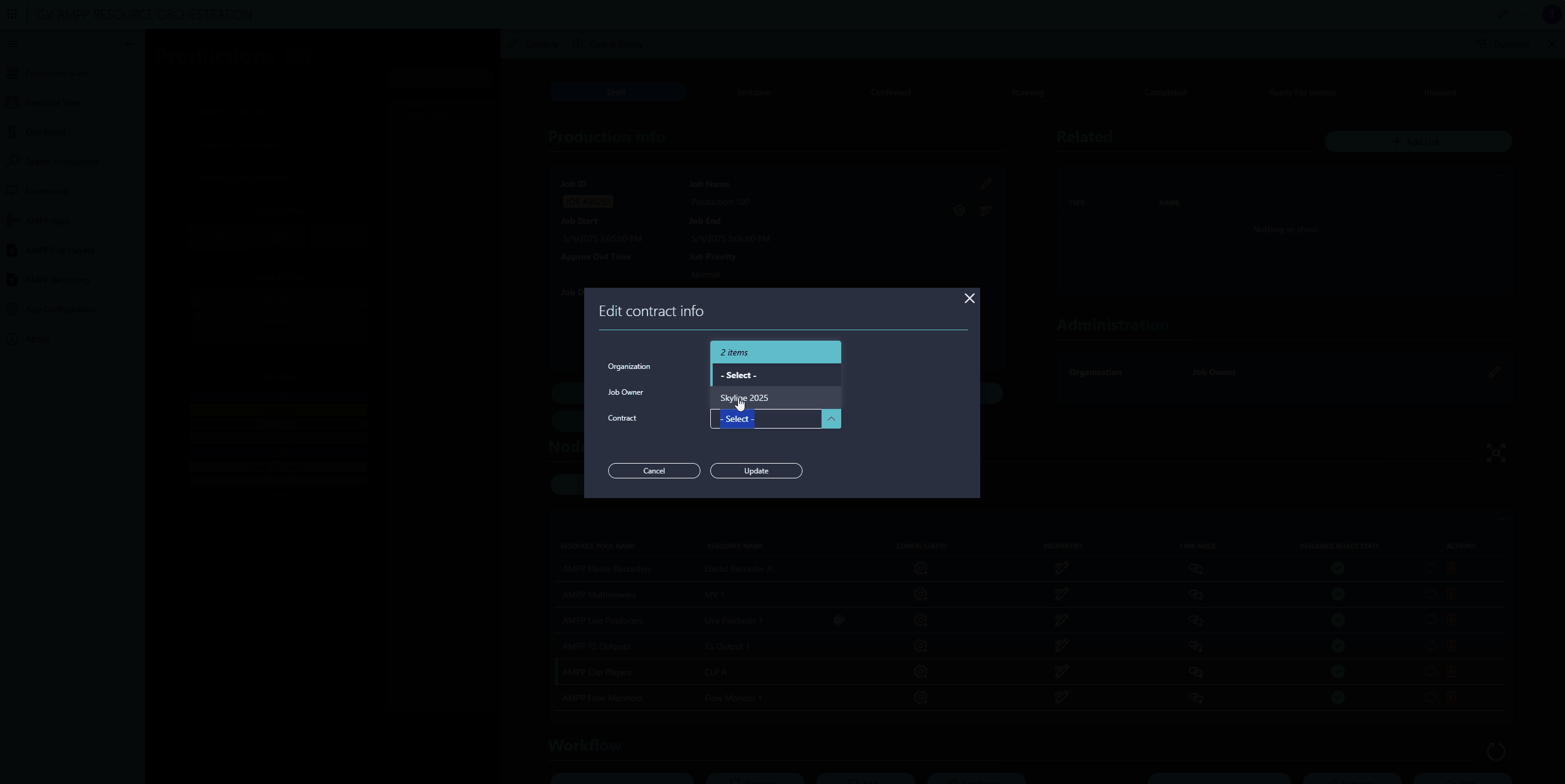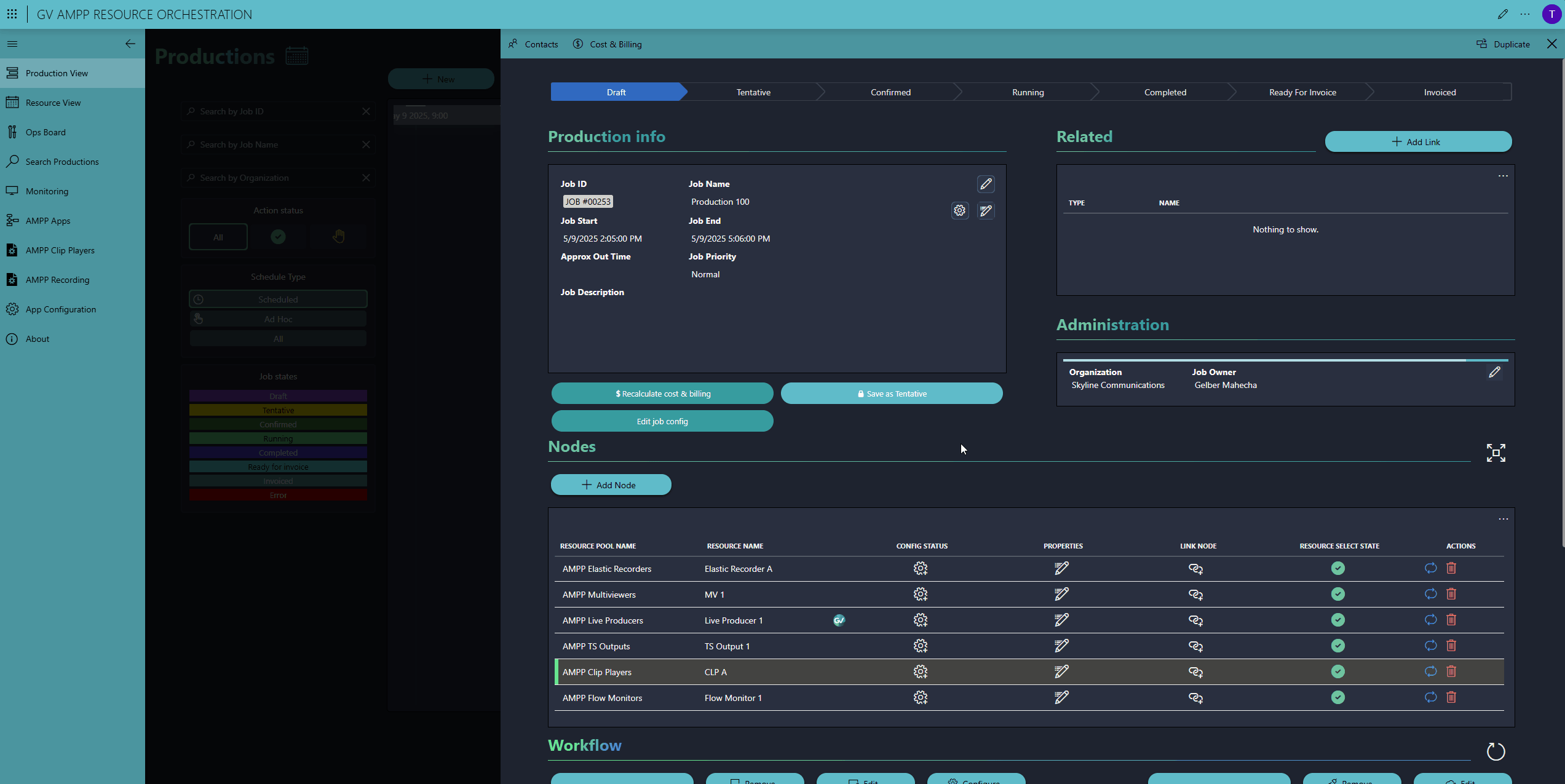 Optionally, operators can assign a contract. Contracts include rate cards for each allocated resource, enabling DataMiner to calculate and track production costs.
Optionally, operators can assign a contract. Contracts include rate cards for each allocated resource, enabling DataMiner to calculate and track production costs.
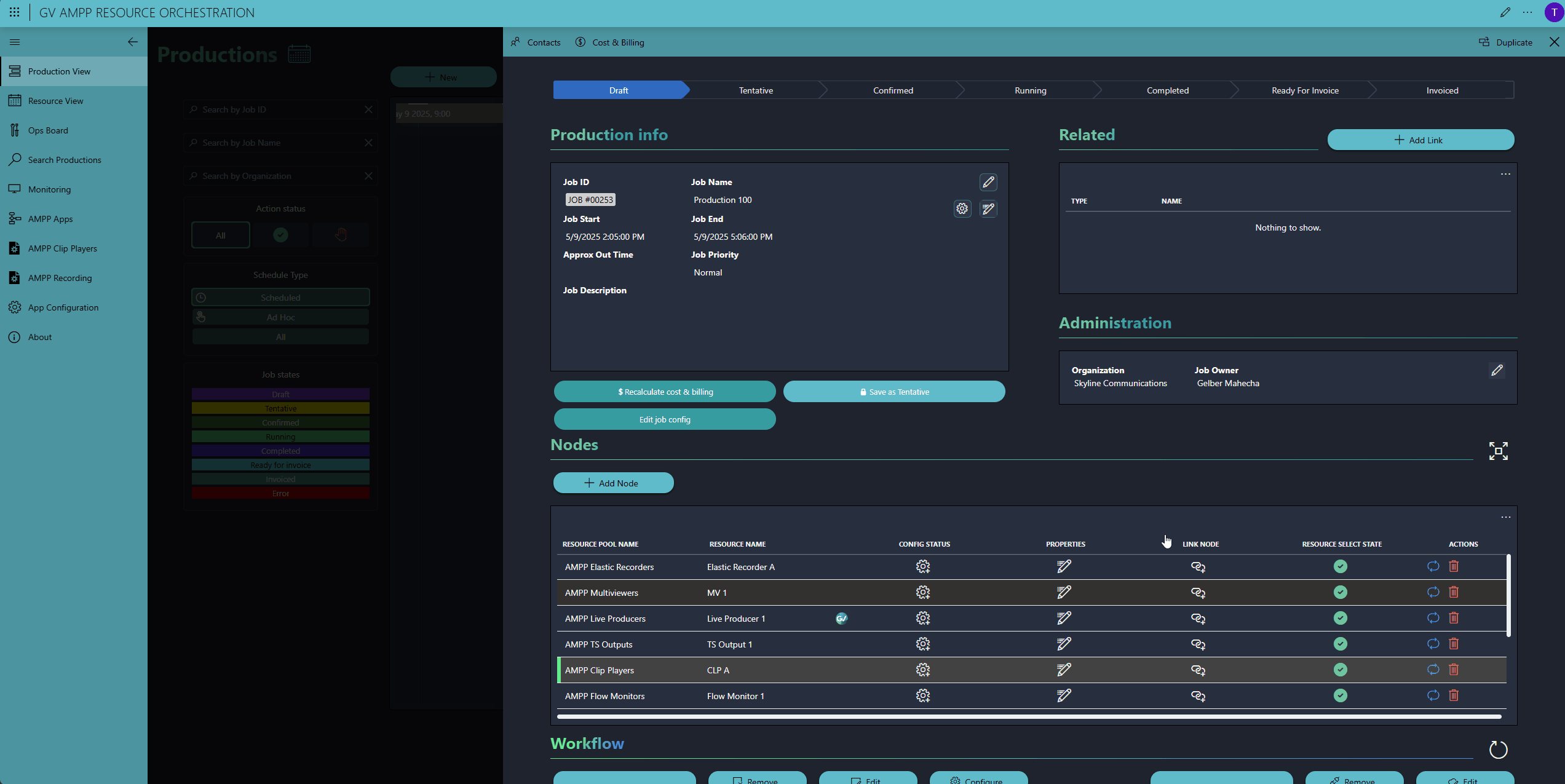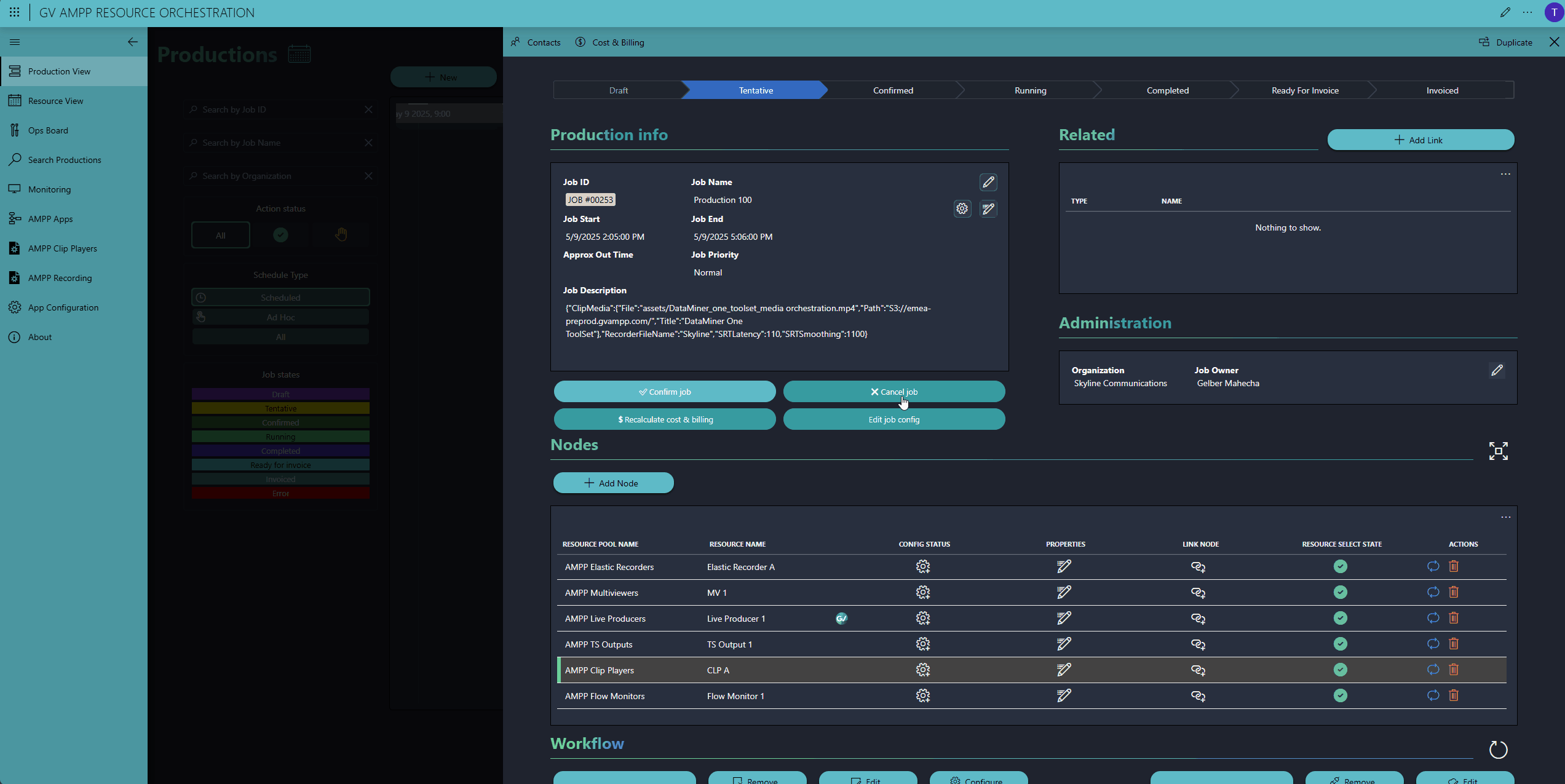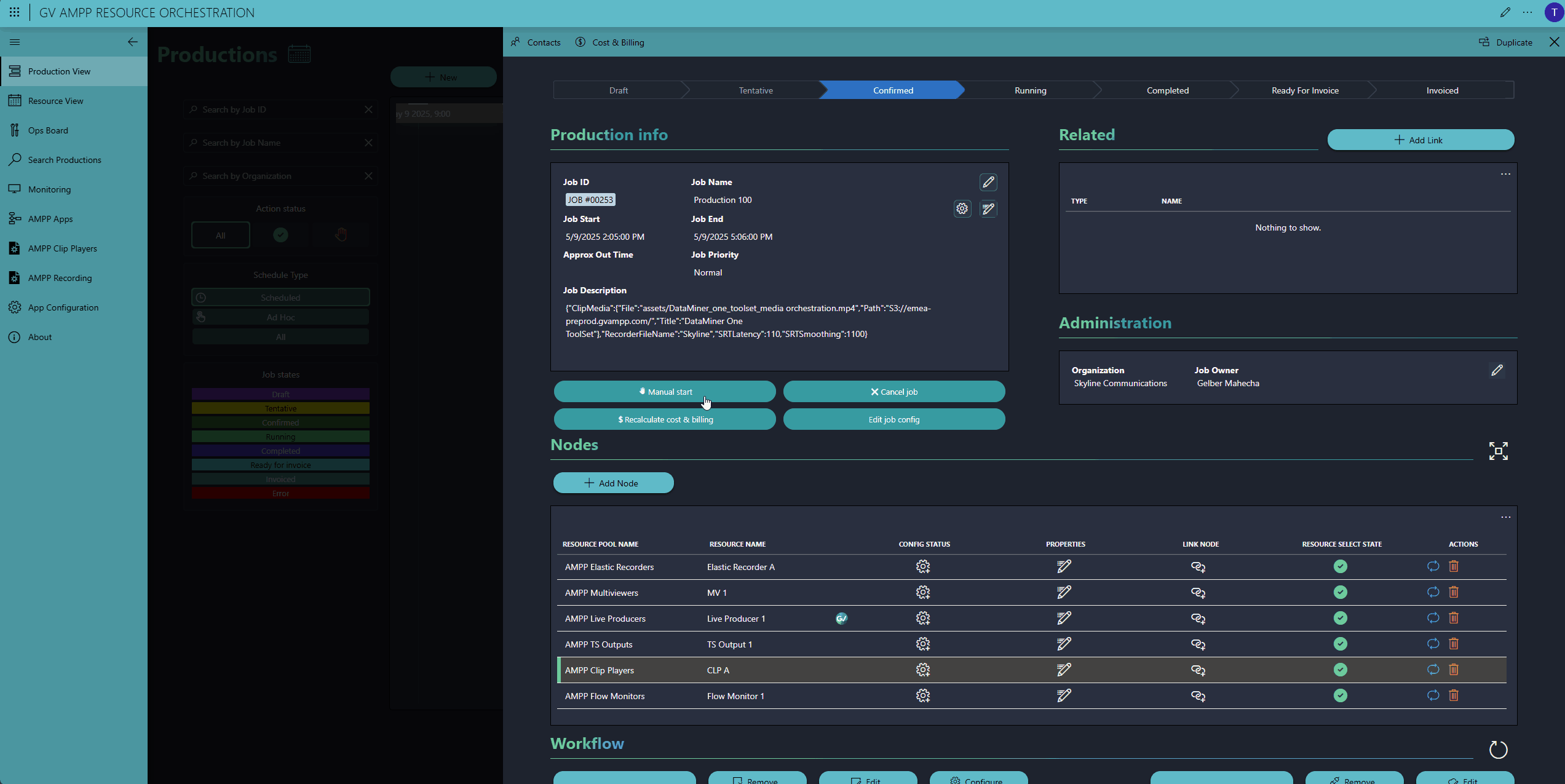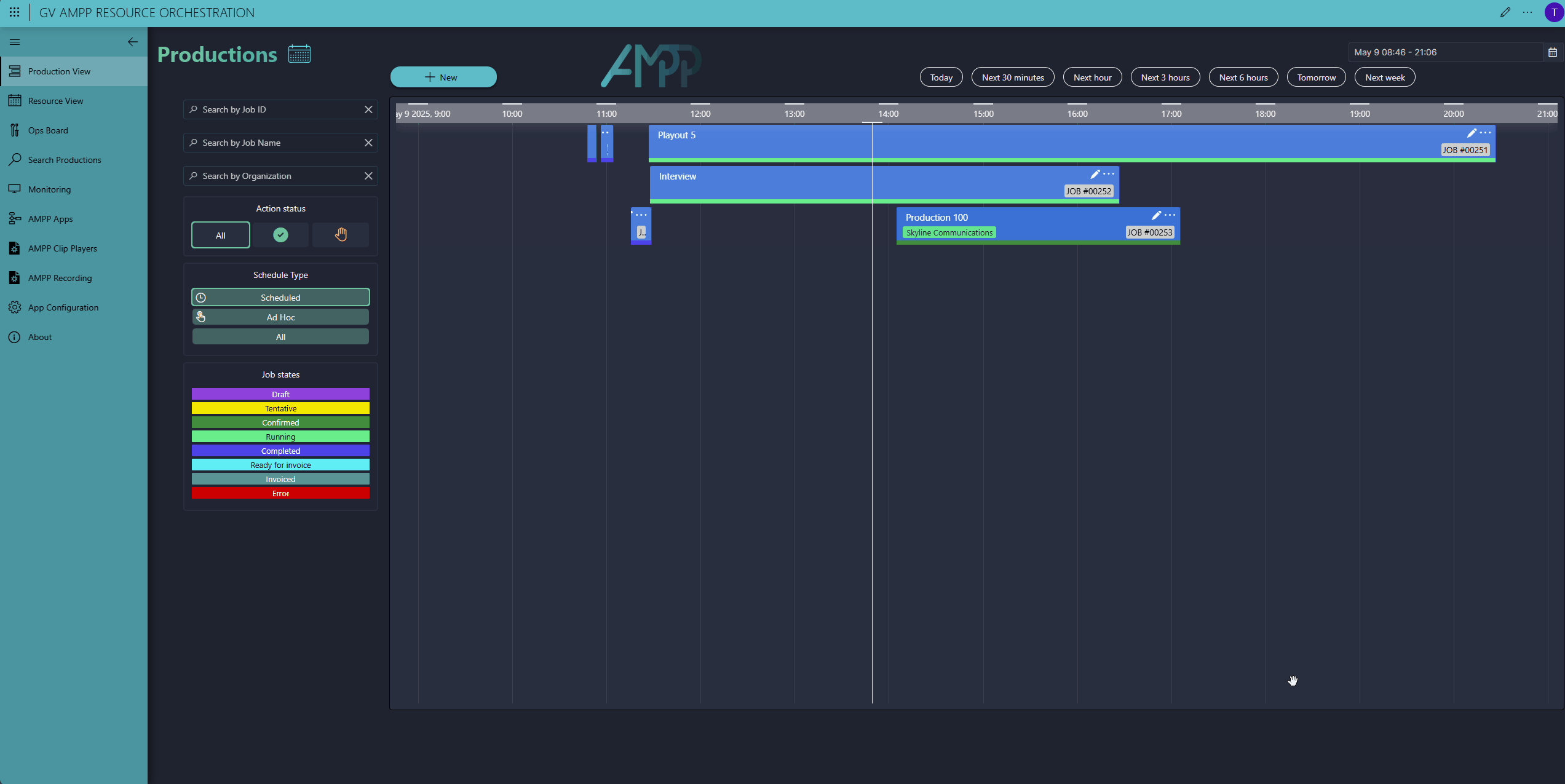 Once everything is configured, simply save and confirm the job. Then lean back—right before the production starts, the DataMiner Automation and Orchestration engine will kicks in to start, configure, and connect all resources.
Once everything is configured, simply save and confirm the job. Then lean back—right before the production starts, the DataMiner Automation and Orchestration engine will kicks in to start, configure, and connect all resources.
 Now let's see what DataMiner does when we get closer to the production start. In this demo, we've triggered it early to speed things up. DataMiner spins up all GV AMPP workloads, configures them, and connects them. We have opened the Grass Valley admin interface to show how everything happens fully automated via DataMiner.
Now let's see what DataMiner does when we get closer to the production start. In this demo, we've triggered it early to speed things up. DataMiner spins up all GV AMPP workloads, configures them, and connects them. We have opened the Grass Valley admin interface to show how everything happens fully automated via DataMiner.
 Our production is now fully up and running: the SRT input into GV AMPP has been configured, the clip player is running, production recording is handled by the Elastic Recorder, and the output from Live Producer is delivered as Transport Stream. As an operator, just open your GV user interface and run your live production. Here, we use a simple GV AMPP Live Producer.
Our production is now fully up and running: the SRT input into GV AMPP has been configured, the clip player is running, production recording is handled by the Elastic Recorder, and the output from Live Producer is delivered as Transport Stream. As an operator, just open your GV user interface and run your live production. Here, we use a simple GV AMPP Live Producer.
 The GV AMPP PGM output is automatically routed to its final destination: a TAG multiviewer. During scheduling, DataMiner has allocated an available multiviewer head from the resource pool. At production start, a multiviewer layout is loaded and all source streams—including the GV AMPP PGM stream—are automatically routed to the multiviewer, as shown in our TAG app.
The GV AMPP PGM output is automatically routed to its final destination: a TAG multiviewer. During scheduling, DataMiner has allocated an available multiviewer head from the resource pool. At production start, a multiviewer layout is loaded and all source streams—including the GV AMPP PGM stream—are automatically routed to the multiviewer, as shown in our TAG app.
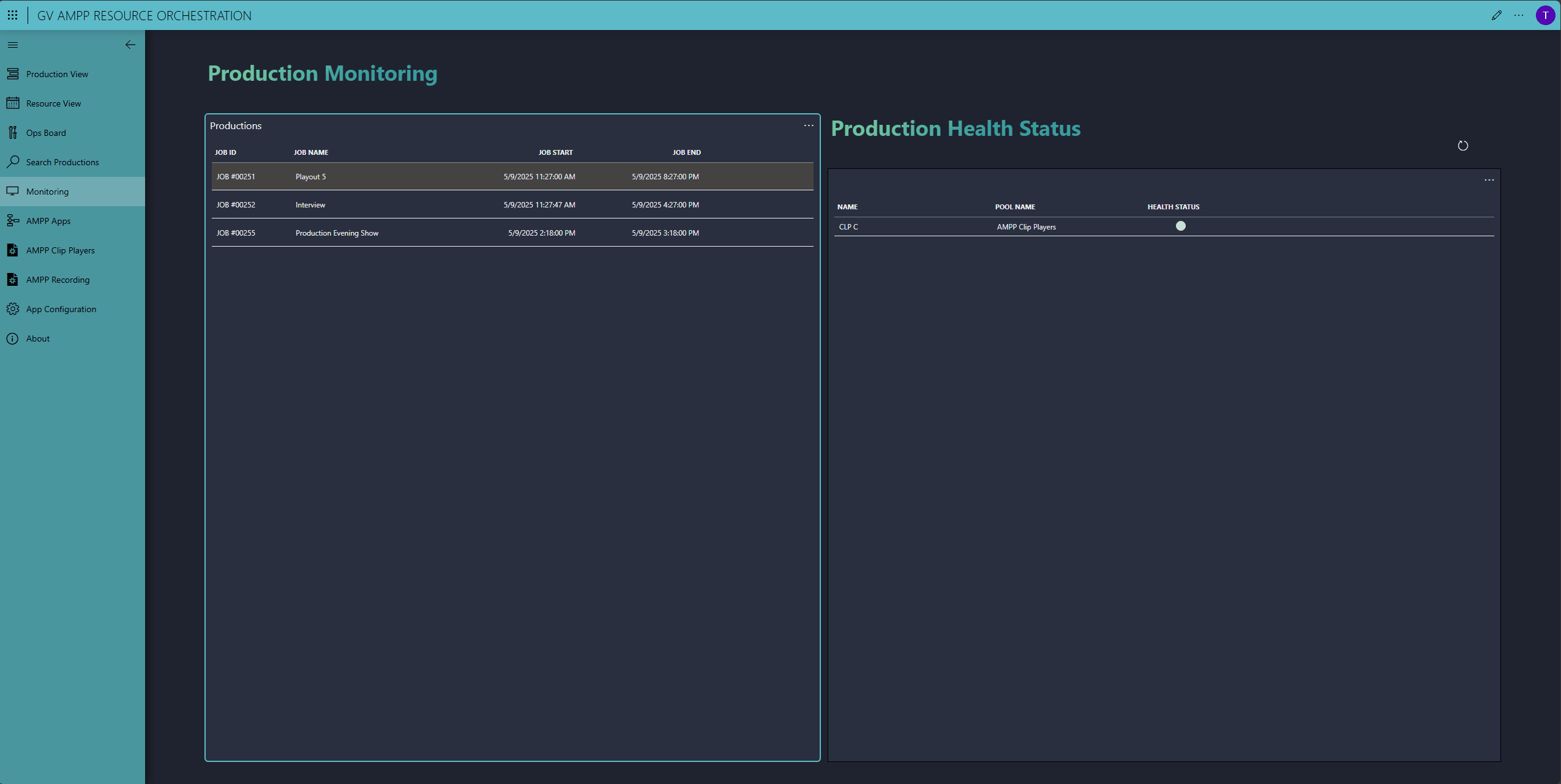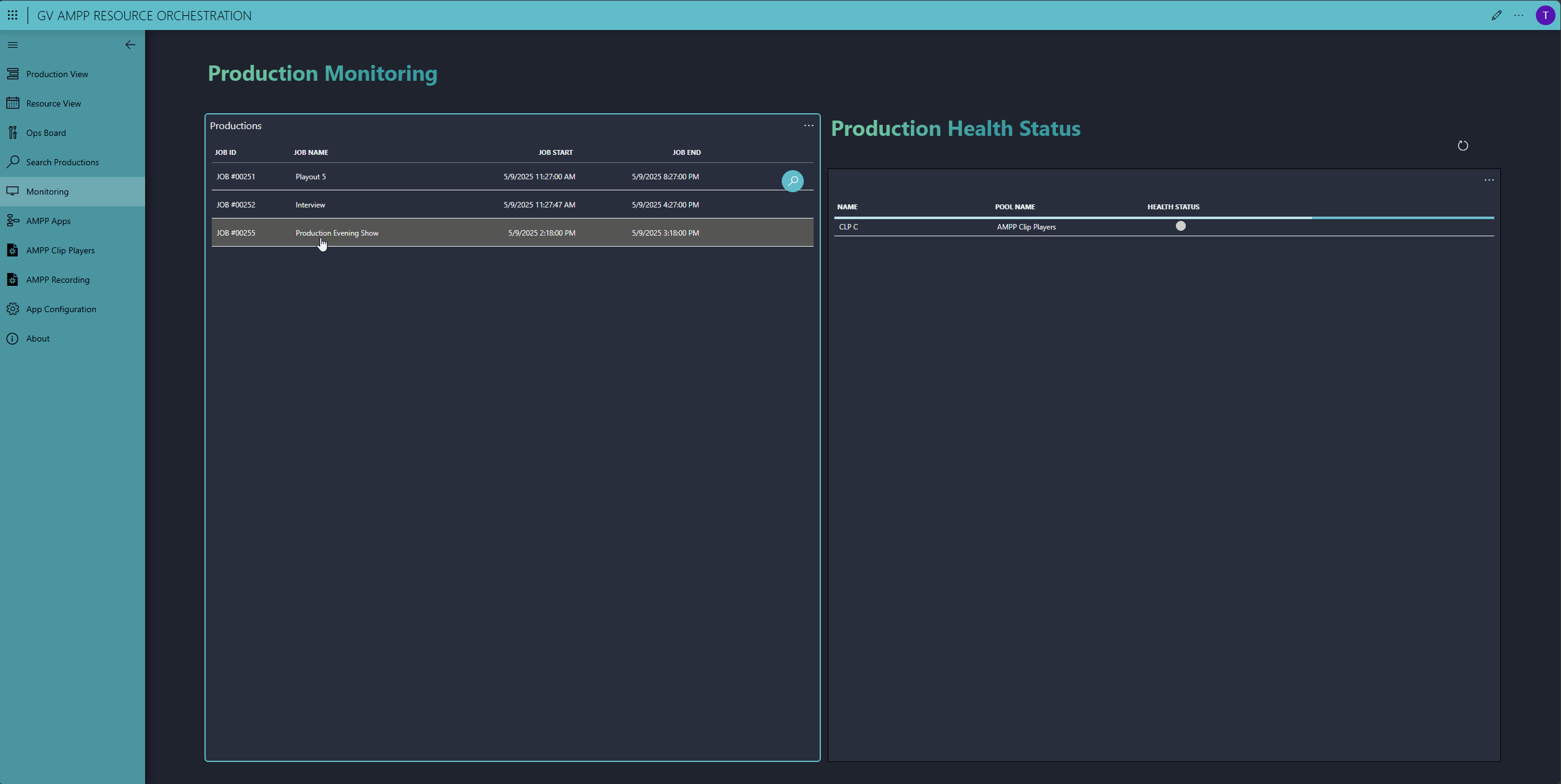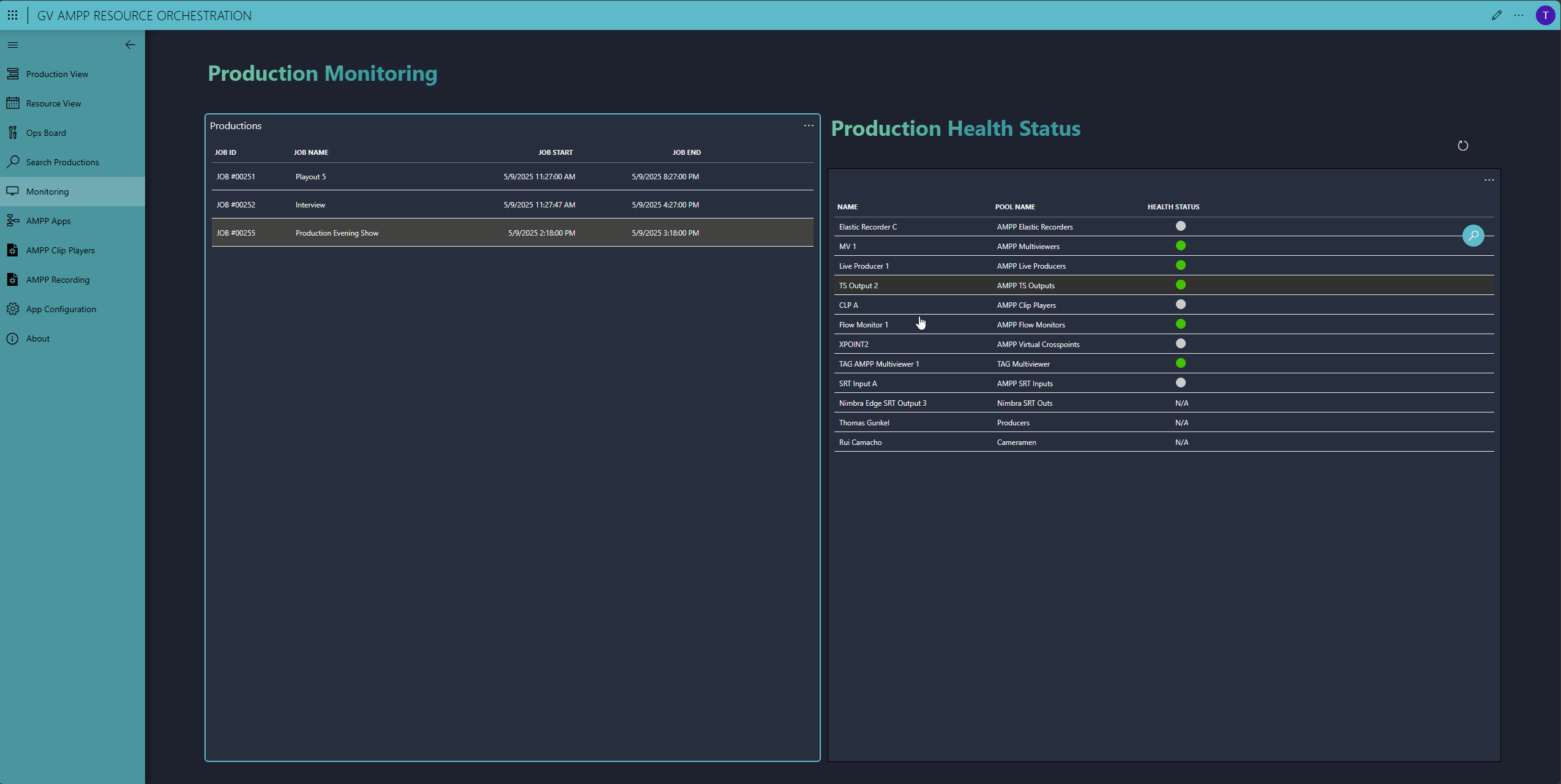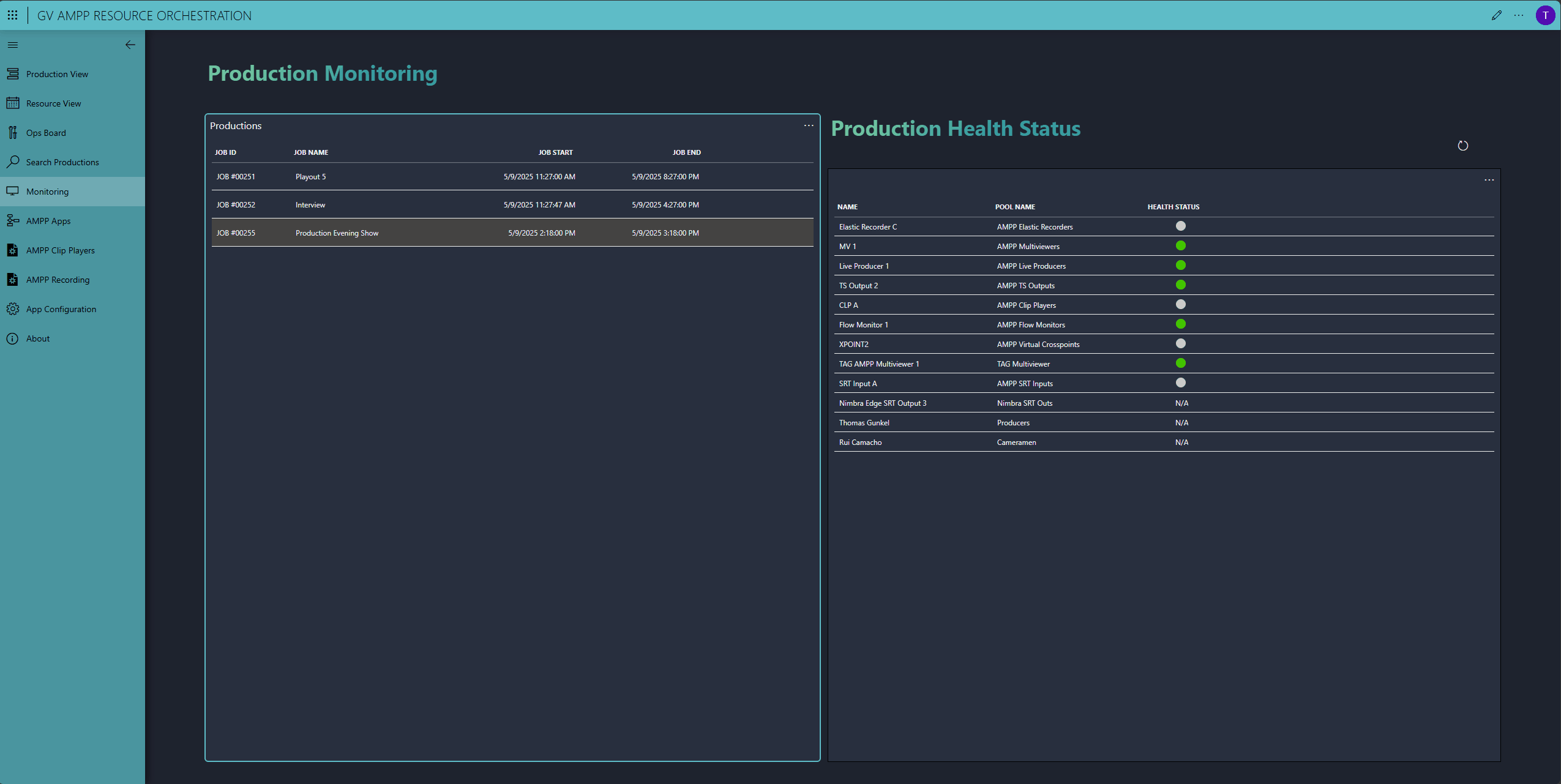 Whilse the production is running, DataMiner monitors all production resources, including the third-party ones from TAG VS and NetInsight.
Whilse the production is running, DataMiner monitors all production resources, including the third-party ones from TAG VS and NetInsight.
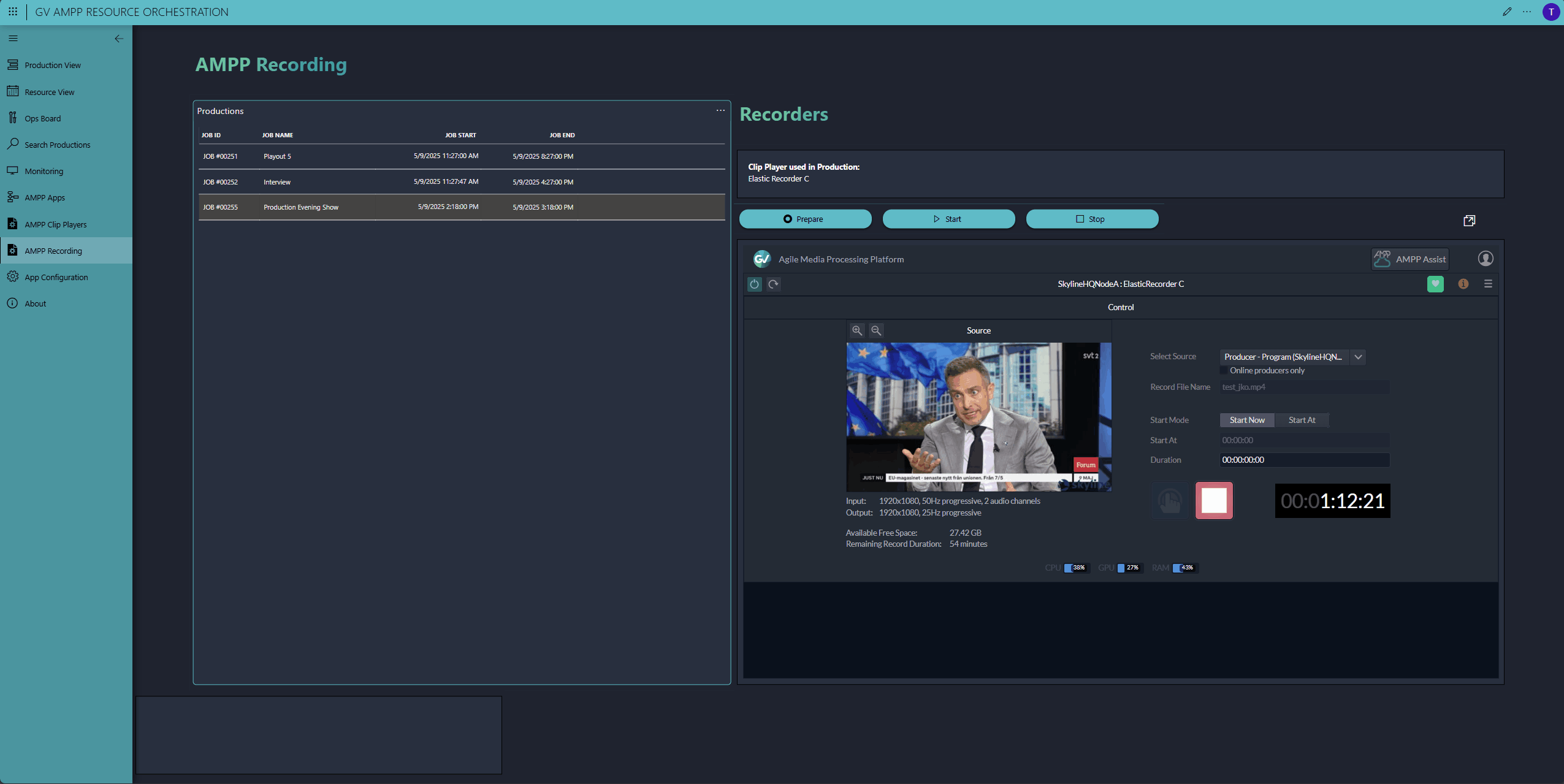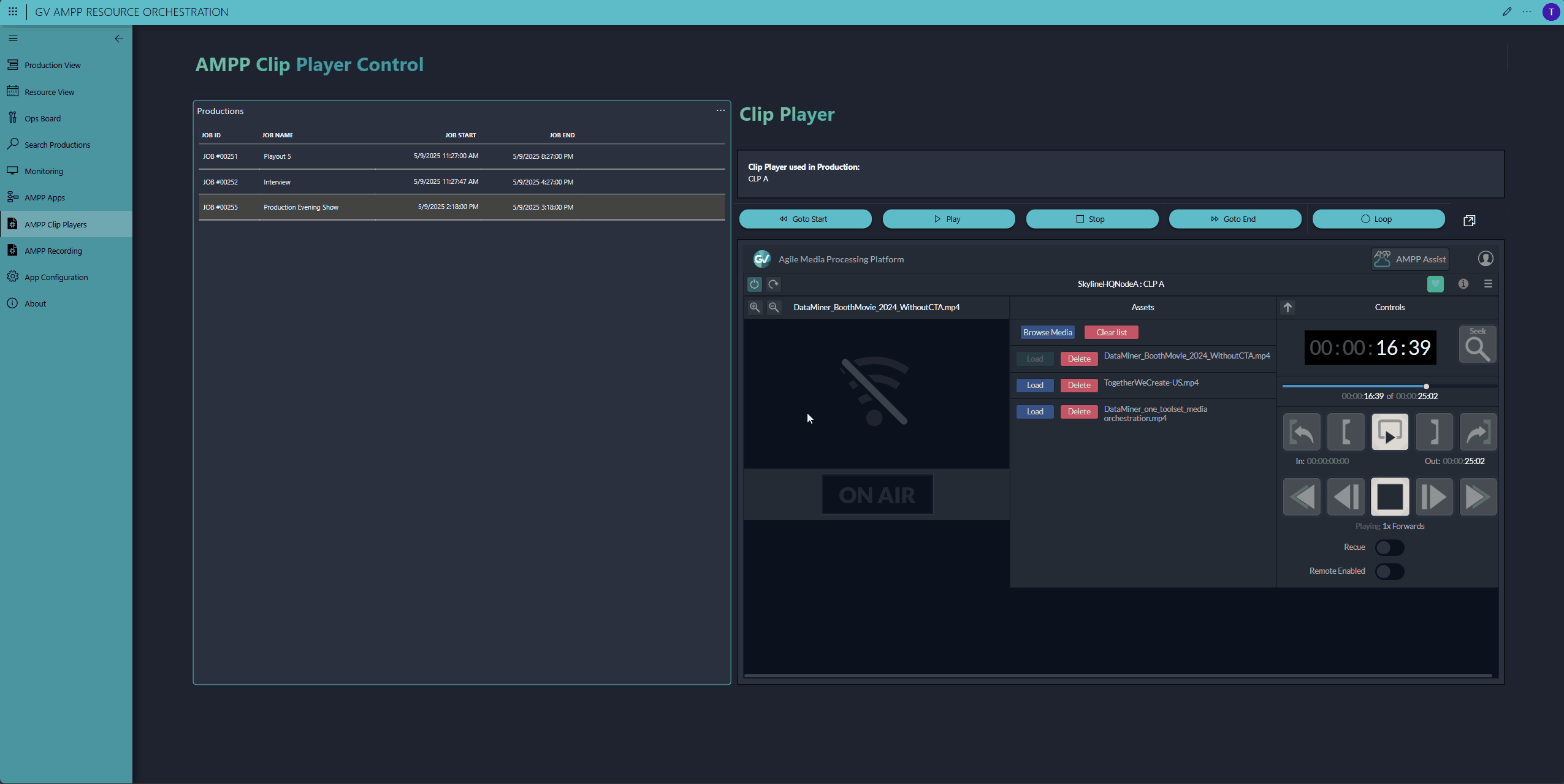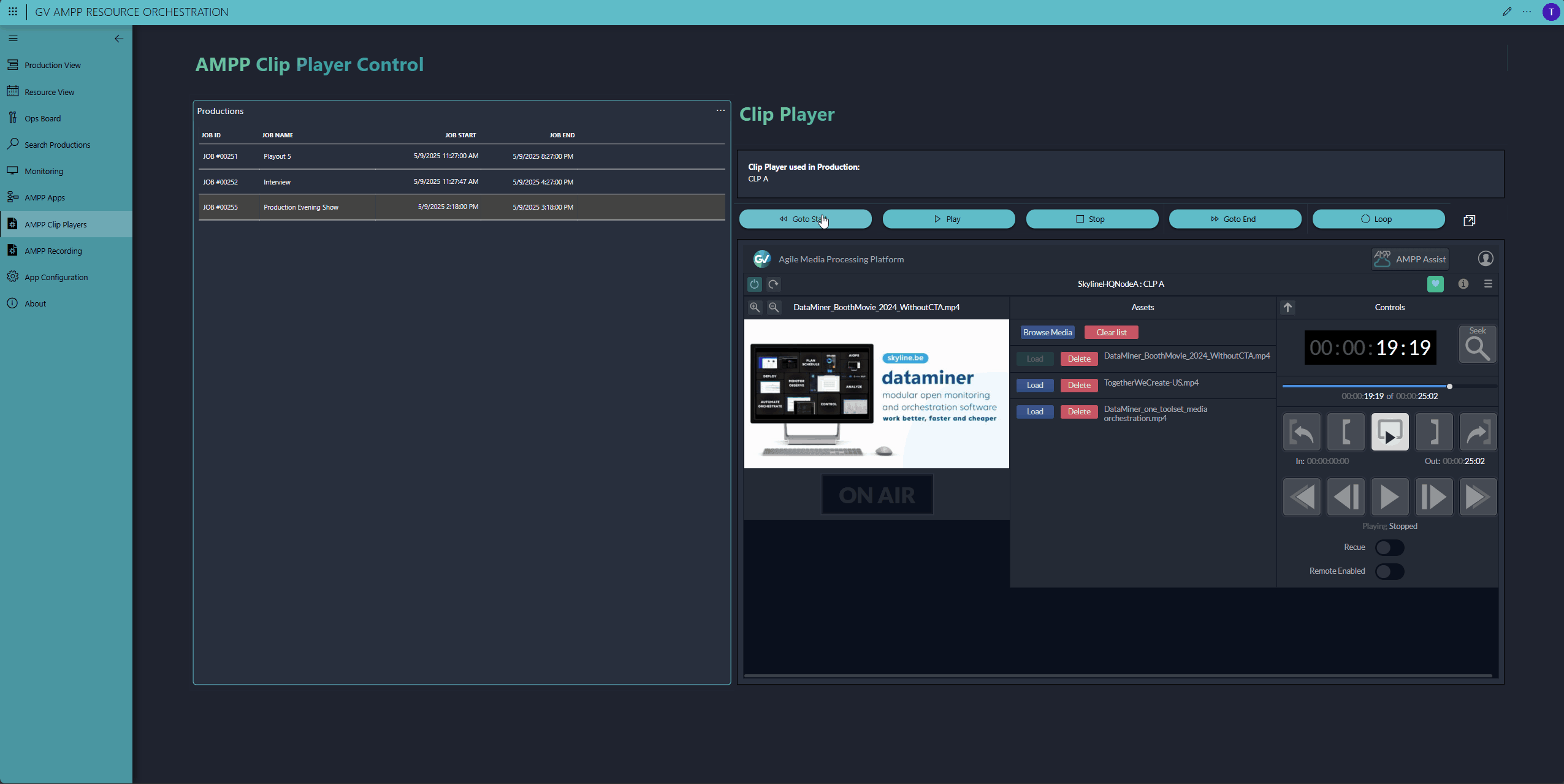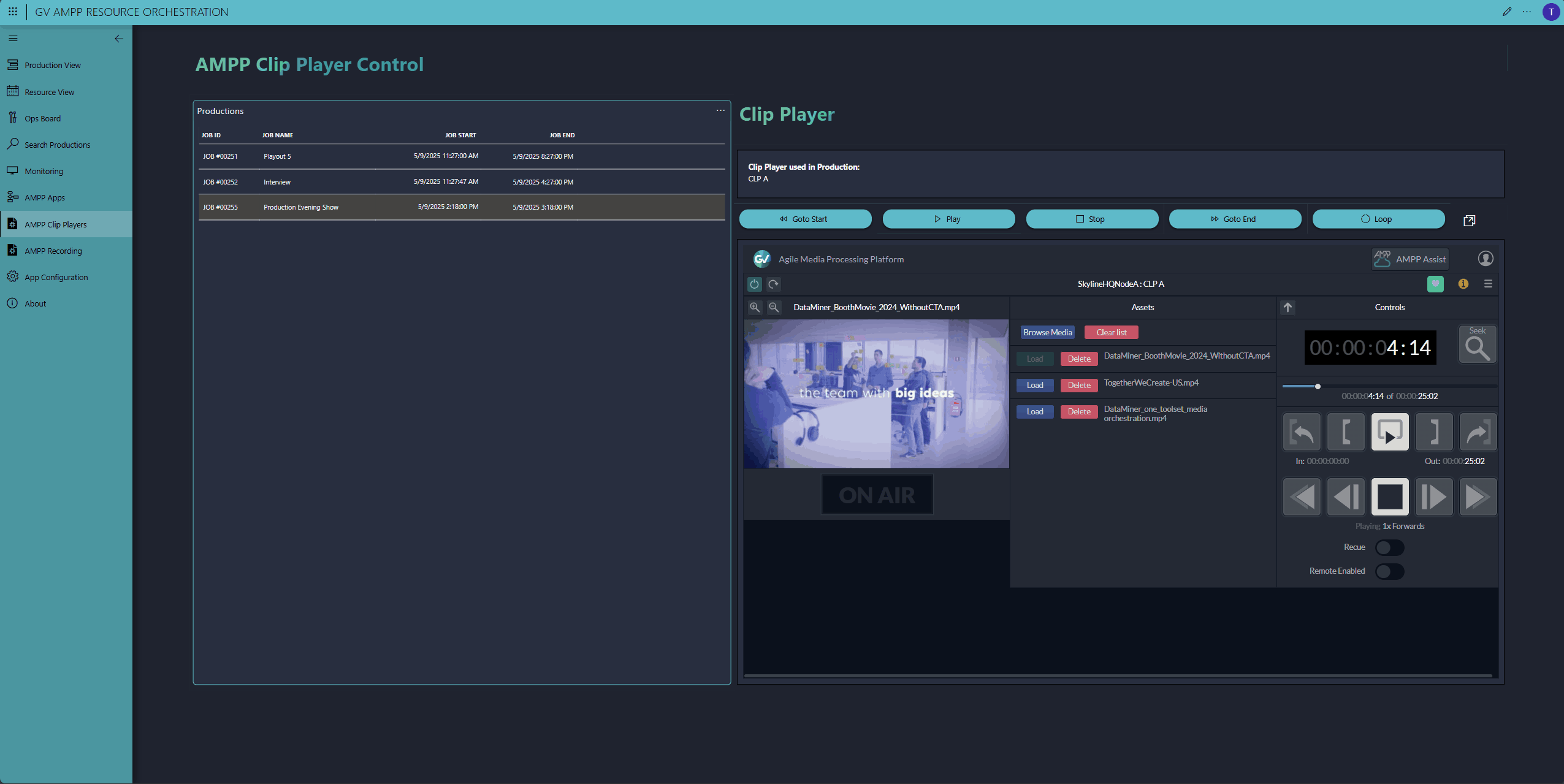 Need a tailored control interface because the default Grass Valley AMPP UIs don't meet your operation's needs? Simply build a DataMiner low-code app with the real-time controls you want. In our demo, we control both GV AMPP players and GV AMPP recorders. We've even embedded an HTML5 GV AMPP component to showcase the real-time control possibilities through DataMiner.
Need a tailored control interface because the default Grass Valley AMPP UIs don't meet your operation's needs? Simply build a DataMiner low-code app with the real-time controls you want. In our demo, we control both GV AMPP players and GV AMPP recorders. We've even embedded an HTML5 GV AMPP component to showcase the real-time control possibilities through DataMiner.
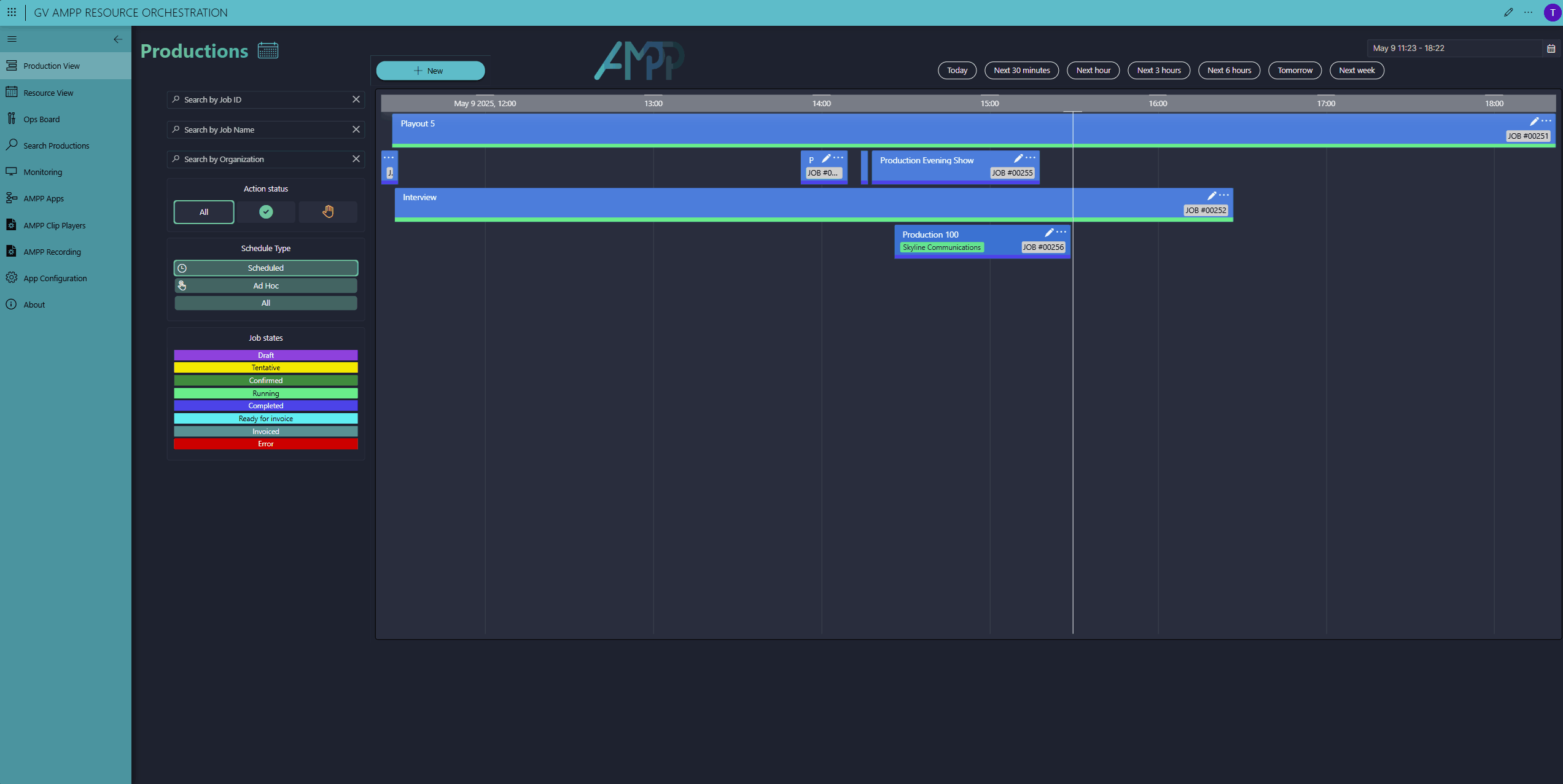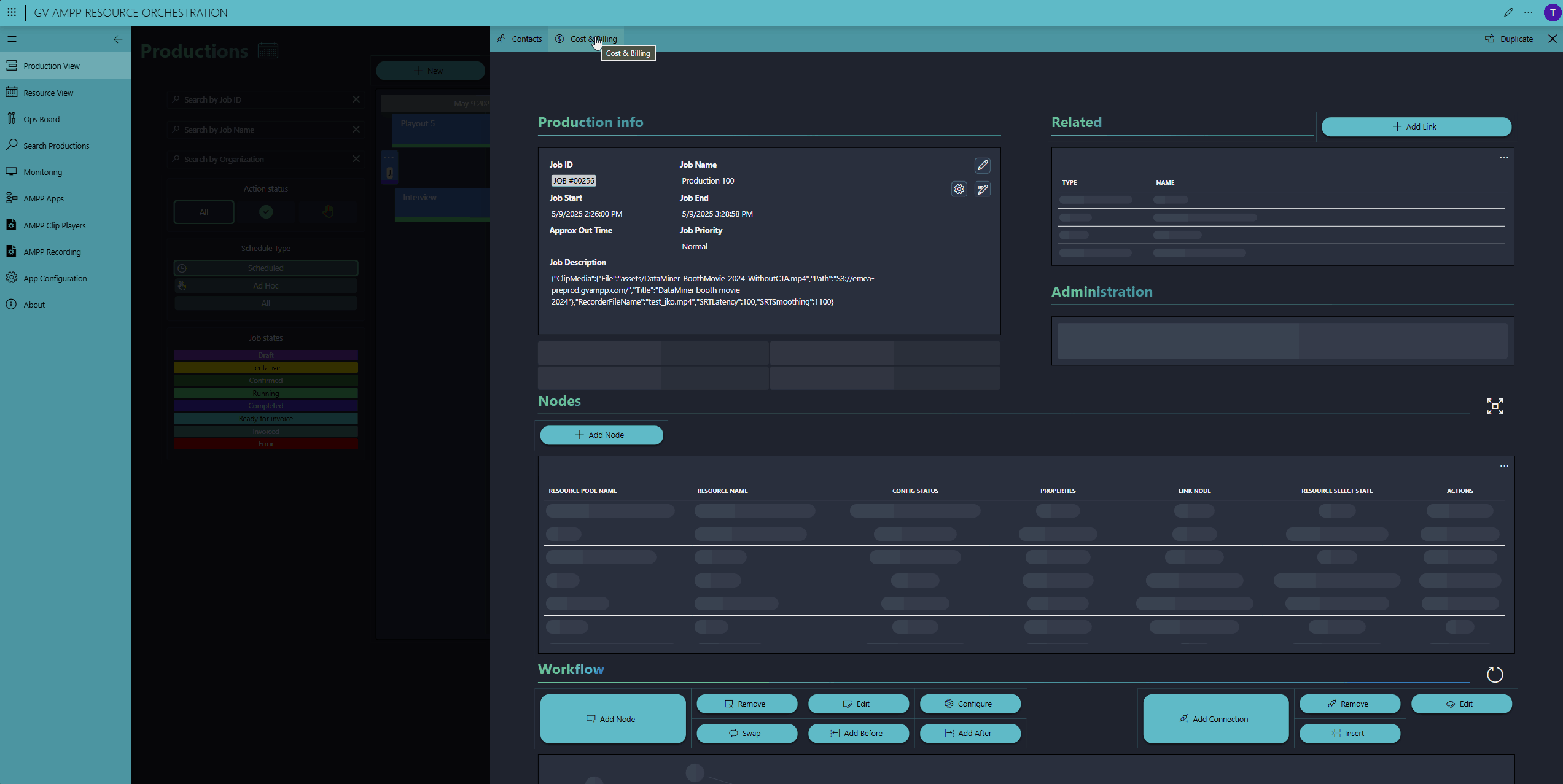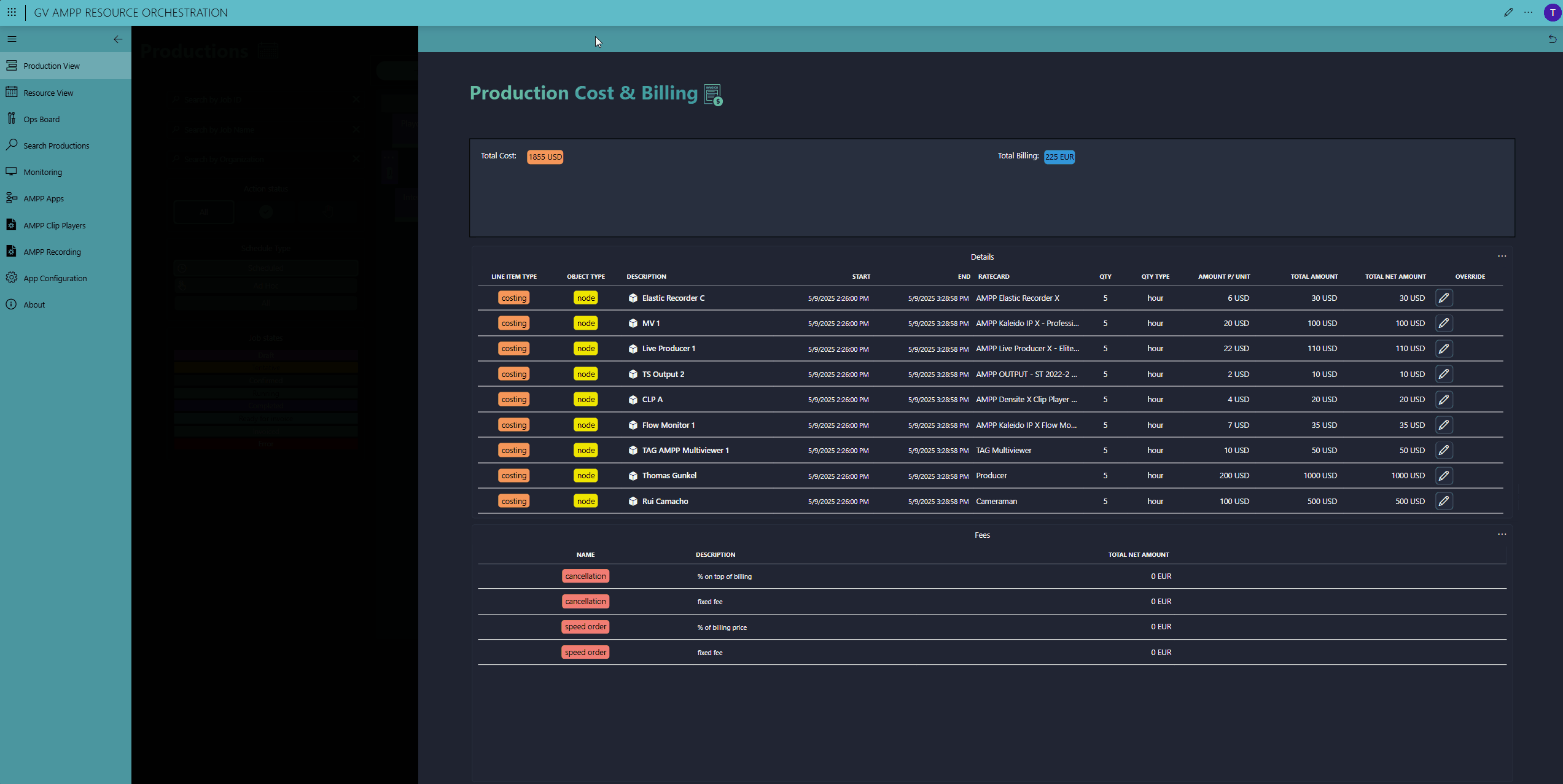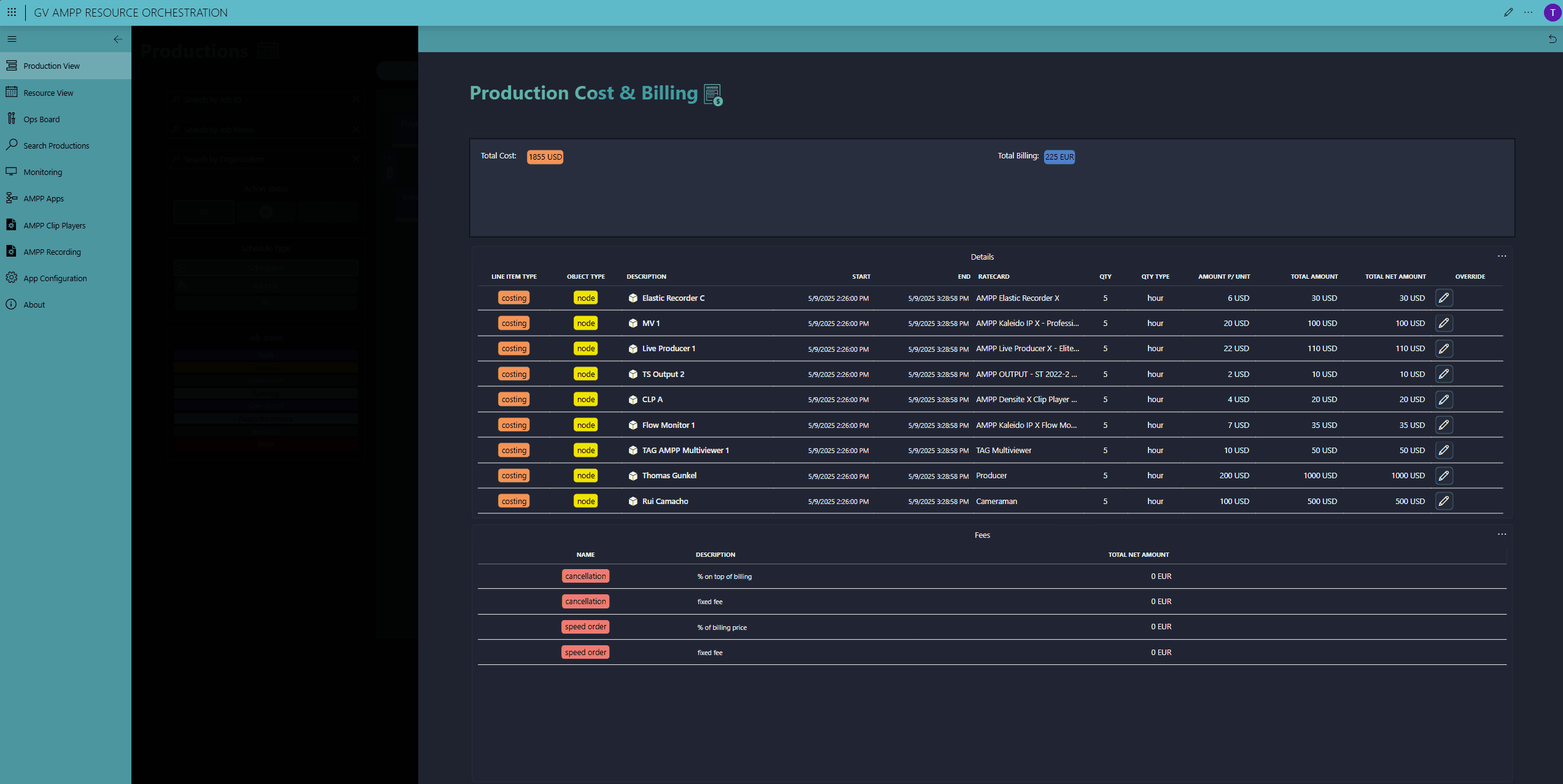 At production end, DataMiner stops all GV AMPP workloads and frees up the resources again. Finally, DataMiner tracks your internal costs and calculates the total production bill using the rate cards attached to the each resource.
At production end, DataMiner stops all GV AMPP workloads and frees up the resources again. Finally, DataMiner tracks your internal costs and calculates the total production bill using the rate cards attached to the each resource.
2 thoughts on “Grass Valley AMPP – Production Scheduling & Orchestration”
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Great post, Thomas! DataMiner is unlocking a wide range of orchestration possibilities ranging from full automated configuration to custom interfaces that allow users to perform a series of actions with the click of a button.
Great work Dataminer team!