Your main and backup links are green—no alarms, no thresholds crossed. Everything looks fine. Yet they’re no longer mirroring each other. Redundancy is already gone, long before anything looks wrong. By the time you notice, the incident is live.
This is exactly the kind of situation Relational Anomaly Detection (RAD) is designed to catch. Monitoring networks is often about monitoring relationships, and DataMiner’s relational AI doesn't just watch individual values. It learns how parameters relate to each other. It knows, for example, that Main and Backup should always track together. If they drift apart, DataMiner alerts you instantly—even if both values still look normal.
Relational Anomaly Detection: in a nutshell
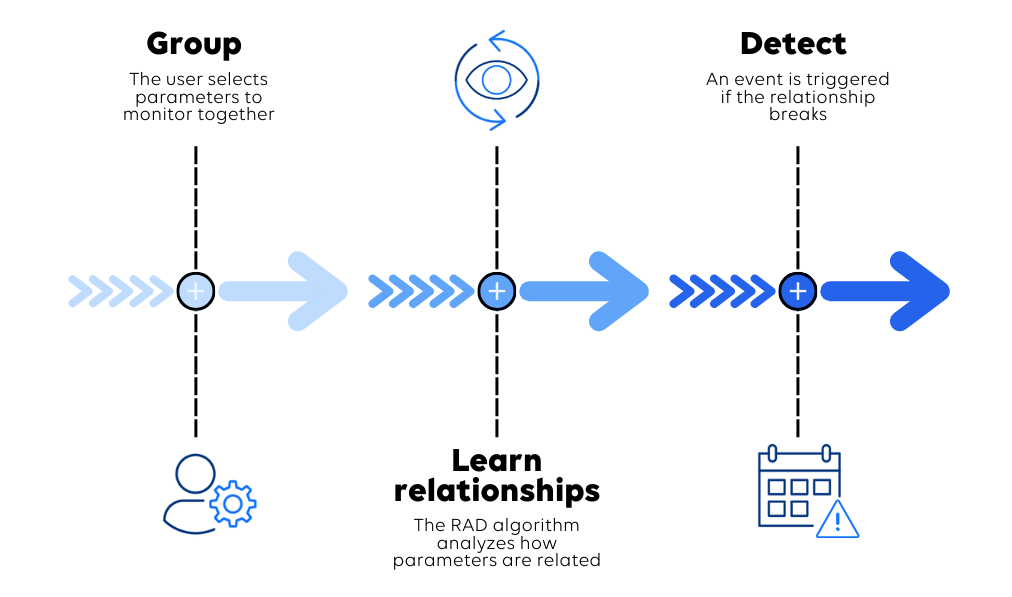
Relational Anomaly Detection (RAD) is DataMiner’s AI capability that monitors how parameters behave together, not just in isolation.
First, you define which parameters belong together, such as Main and Backup bitrates. Next, DataMiner automatically learns the normal relationship between them. Once that baseline is established, RAD detects when the relationship breaks—even if both values are still within the expected ranges.
Where RAD adds value
RAD has been successfully battle-tested across many real-life use cases. It consistently catches issues that traditional threshold-based monitoring misses. Here are just some of them:
| If you monitor... | RAD helps you by... |
|---|---|
| Main & Backup paths | Alerting you the moment the backup stops mirroring the main. |
| UPS & battery banks | Identifying cells or units that deviate from the rest, so batteries can be replaced based on health instead of risky discharge tests. |
| Bonded interfaces | Spotting when one link in the group is underperforming or degraded. |
| Hardware health | Correlating fan speed with temperature to detect failing components early. |
| HVAC monitoring | Detecting abnormal AC current draw relative to temperature, revealing failing compressors or sensors. |
| Transmitters | Detecting interference or rain fades by comparing C/N values with RF input levels. |
What’s new in the upcoming Main Release?
With DataMiner Main Release 10.6.0, RAD moves from a specialized feature to a core capability. This release includes a completely refactored RAD Manager app, built for speed and scale.
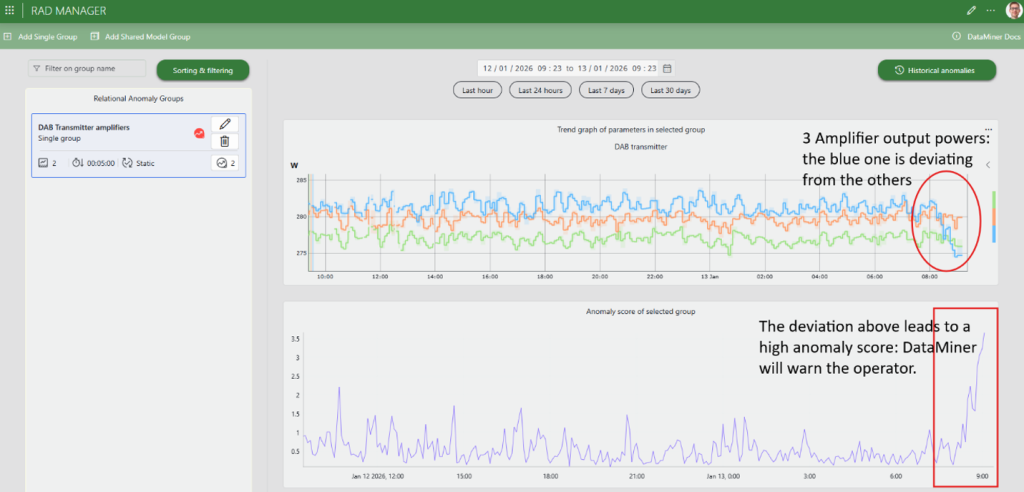
The RAD Manager app provides a dedicated and intuitive UI to configure groups, manage models, and visualize historical anomaly scores within seconds.
Shared model groups make it possible to monitor large fleets efficiently. Do you have 500 identical UPS units or 100 encoders? No matter. A single shared model can now be used across the entire fleet, ensuring consistency and drastically reducing computational overhead.
Fleet outlier detection adds another layer by automatically highlighting which specific device behaves differently from its peers. This makes it easier to prioritize maintenance where it's actually needed. You could call this a real "needle in the haystack" finder.
Get started today
You don't need a data science degree to start using AI-powered monitoring.
- Check your version: Ensure you are running the latest DataMiner Main Release (10.6.0 or higher).
- Install the RAD Manager: Download the RAD Manager app directly from the DataMiner Catalog.
- Create your first group: Start with a simple group, such as a Main vs. Backup bitrate pair, and see the anomaly scores in action.
- Let RAD do the work: RAD alerts you when parameters in the group are behaving unexpectedly.
For more information about relational anomaly detection and a guide to installing and using the RAD Manager app, visit the official DataMiner documentation.